Epigenetic Induction of Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Alterations in Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections
- PMID: 37555319
- PMCID: PMC10529114
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.063332
Epigenetic Induction of Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Alterations in Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections
Abstract
Background: Smooth muscle cell (SMC) phenotypic switching has been increasingly detected in aortic aneurysm and dissection (AAD) tissues. However, the diverse SMC phenotypes in AAD tissues and the mechanisms driving SMC phenotypic alterations remain to be identified.
Methods: We examined the transcriptomic and epigenomic dynamics of aortic SMC phenotypic changes in mice with angiotensin II-induced AAD by using single-cell RNA sequencing and single-cell sequencing assay for transposase-accessible chromatin. SMC phenotypic alteration in aortas from patients with ascending thoracic AAD was examined by using single-cell RNA sequencing analysis.
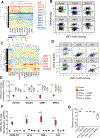
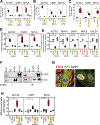
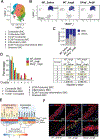
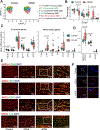
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis revealed that aortic stress induced the transition of SMCs from a primary contractile phenotype to proliferative, extracellular matrix-producing, and inflammatory phenotypes. Lineage tracing showed the complete transformation of SMCs to fibroblasts and macrophages. Single-cell sequencing assay for transposase-accessible chromatin analysis indicated that these phenotypic alterations were controlled by chromatin remodeling marked by the reduced chromatin accessibility of contractile genes and the induced chromatin accessibility of genes involved in proliferation, extracellular matrix, and inflammation. IRF3 (interferon regulatory factor 3), a proinflammatory transcription factor activated by cytosolic DNA, was identified as a key driver of the transition of aortic SMCs from a contractile phenotype to an inflammatory phenotype. In cultured SMCs, cytosolic DNA signaled through its sensor STING (stimulator of interferon genes)-TBK1 (tank-binding kinase 1) to activate IRF3, which bound and recruited EZH2 (enhancer of zeste homolog 2) to contractile genes to induce repressive H3K27me3 modification and gene suppression. In contrast, double-stranded DNA-STING-IRF3 signaling induced inflammatory gene expression in SMCs. In Sting-/- mice, the aortic stress-induced transition of SMCs into an inflammatory phenotype was prevented, and SMC populations were preserved. Finally, profound SMC phenotypic alterations toward diverse directions were detected in human ascending thoracic AAD tissues.
Conclusions: Our study reveals the dynamic epigenetic induction of SMC phenotypic alterations in AAD. DNA damage and cytosolic leakage drive SMCs from a contractile phenotype to an inflammatory phenotype.
Keywords: DNA damage; STING1 protein, human; aortic aneurysm; aortic dissection; chromatin remodeling; muscle, smooth, vascular; phenotype.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Owens GK. Regulation of differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:487–517. - PubMed
-
- Stegemann JP, Hong H, Nerem RM. Mechanical, biochemical, and extracellular matrix effects on vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005;98:2321–2327. - PubMed
-
- Petsophonsakul P, Furmanik M, Forsythe R, Dweck M, Schurink GW, Natour E, Reutelingsperger C, Jacobs M, Mees B, Schurgers L. Role of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and calcification in aortic aneurysm formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39:1351–1368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL143359/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025240/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133254/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023469/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125632/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159988/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM138407/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018033/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES030285/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131980/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158157/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HG010442/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

