An open-source platform for head-fixed operant and consummatory behavior
- PMID: 37555578
- PMCID: PMC10499376
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.86183
An open-source platform for head-fixed operant and consummatory behavior
Abstract
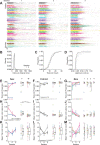
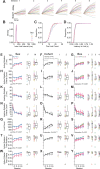
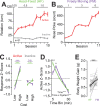
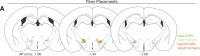
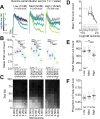
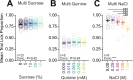
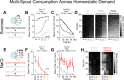
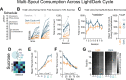
Head-fixed behavioral experiments in rodents permit unparalleled experimental control, precise measurement of behavior, and concurrent modulation and measurement of neural activity. Here, we present OHRBETS (Open-Source Head-fixed Rodent Behavioral Experimental Training System; pronounced 'Orbitz'), a low-cost, open-source platform of hardware and software to flexibly pursue the neural basis of a variety of motivated behaviors. Head-fixed mice tested with OHRBETS displayed operant conditioning for caloric reward that replicates core behavioral phenotypes observed during freely moving conditions. OHRBETS also permits optogenetic intracranial self-stimulation under positive or negative operant conditioning procedures and real-time place preference behavior, like that observed in freely moving assays. In a multi-spout brief-access consumption task, mice displayed licking as a function of concentration of sucrose, quinine, and sodium chloride, with licking modulated by homeostatic or circadian influences. Finally, to highlight the functionality of OHRBETS, we measured mesolimbic dopamine signals during the multi-spout brief-access task that display strong correlations with relative solution value and magnitude of consumption. All designs, programs, and instructions are provided freely online. This customizable platform enables replicable operant and consummatory behaviors and can be incorporated with methods to perturb and record neural dynamics in vivo.
Keywords: ingestive behavior; motivation; mouse; neuroscience; reward.
© 2023, Gordon-Fennell et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AG, JB, MU, SS, PB, RG, MB, MR, GS No competing interests declared
Figures












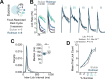


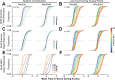




Update of
-
An Open-Source Platform for Head-Fixed Operant and Consummatory Behavior.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 16:2023.01.13.523828. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.13.523828. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Aug 09;12:e86183. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86183. PMID: 36712040 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Studying behavior under constrained movement.Elife. 2023 Aug 30;12:e91145. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91145. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37646772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguillon-Rodriguez V, Angelaki D, Bayer H, Bonacchi N, Carandini M, Cazettes F, Chapuis G, Churchland AK, Dan Y, Dewitt E, Faulkner M, Forrest H, Haetzel L, Häusser M, Hofer SB, Hu F, Khanal A, Krasniak C, Laranjeira I, Mainen ZF, Meijer G, Miska NJ, Mrsic-Flogel TD, Murakami M, Noel J-P, Pan-Vazquez A, Rossant C, Sanders J, Socha K, Terry R, Urai AE, Vergara H, Wells M, Wilson CJ, Witten IB, Wool LE, Zador AM, The International Brain Laboratory Standardized and reproducible measurement of decision-making in mice. eLife. 2021;10:e63711. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Backyard Brains Searcher- 3-D Printable Micromanipulator. 2013. [December 3, 2020]. https://backyardbrains.com/products/micromanipulator
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

