The Role of CCL24 in Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 37555717
- PMCID: PMC10393469
- DOI: 10.5041/RMMJ.10504
The Role of CCL24 in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
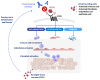
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic immune-mediated disease characterized by microangiopathy, immune dysregulation, and progressive fibrosis of the skin and internal organs. Though not fully understood, the pathogenesis of SSc is dominated by microvascular injury, endothelial dysregulation, and immune response that are thought to be associated with fibroblast activation and related fibrogenesis. Among the main clinical subsets, diffuse SSc (dSSc) is a progressive form with rapid and disseminated skin thickening accompanied by internal organ fibrosis and dysfunction. Despite recent advances and multiple randomized clinical trials in early dSSc patients, an effective disease-modifying treatment for progressive skin fibrosis is still missing, and there is a crucial need to identify new targets for therapeutic intervention. Eotaxin-2 (CCL24) is a chemokine secreted by immune cells and epithelial cells, which promotes trafficking of immune cells and activation of pro-fibrotic cells through CCR3 receptor binding. Higher levels of CCL24 and CCR3 were found in the skin and sera of patients with SSc compared with healthy controls; elevated levels of CCL24 and CCR3 were associated with fibrosis and predictive of greater lung function deterioration. Growing evidence supports the potency of a CCL24-blocking antibody as an anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic modulating agent in multiple preclinical models that involve liver, skin, and lung inflammation and fibrosis. This review highlights the role of CCL24 in orchestrating immune, vascular, and fibrotic pathways, and the potential of CCL24 inhibition as a novel treatment for SSc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

