Breast MRI in patients with implantable loop recorder: initial experience
- PMID: 37555957
- PMCID: PMC11181953
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-023-10025-3
Breast MRI in patients with implantable loop recorder: initial experience
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the feasibility of breast MRI exams and guided biopsies in patients with an implantable loop recorder (ILR) as well as the impact ILRs may have on image interpretation.
Materials and methods: This retrospective study examined breast MRIs of patients with ILR, from April 2008 to September 2022. Radiological reports and electronic medical records were reviewed for demographic characteristics, safety concerns, and imaging findings. MR images were analyzed and compared statistically for artifact quantification on the various pulse sequences.
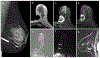
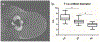
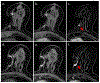
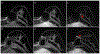
Results: Overall, 40/82,778 (0.049%) MRIs during the study period included ILR. All MRIs were completed without early termination. No patient-related or device-related adverse events occurred. ILRs were most commonly located in the left lower-inner quadrant (64.6%). The main artifact was a signal intensity (SI) void in a dipole formation in the ILR bed with or without areas of peripheral high SI. Artifacts appeared greatest in the cranio-caudal axis (p < 0.001), followed by the anterior-posterior axis (p < 0.001), and then the right-left axis. High peripheral rim-like SI artifacts appeared on the post-contrast and subtracted T1-weighted images, mimicking suspicious enhancement. Artifacts were most prominent on diffusion-weighted (p < 0.001), followed by T2-weighted and T1-weighted images. In eight patients, suspicious findings were found on MRI, resulting in four additional malignant lesions. Of six patients with left breast cancer, the tumor was completely visible in five cases and partially obscured in one.
Conclusion: Breast MRI is feasible and safe among patients with ILR and may provide a significant diagnostic value, albeit with localized, characteristic artifacts.
Clinical relevance statement: Indicated breast MRI exams and guided biopsies can be safely performed in patients with implantable loop recorder. Nevertheless, radiologists should be aware of associated limitations including limited assessment of the inner left breast and pseudo-enhancement artifacts.
Key points: • Breast MRI in patients with an implantable loop recorder is an infrequent, feasible, and safe procedure. • Despite limited breast visualization of the implantable loop recorder bed and characteristic artifacts, MRI depicted additional lesions in 8/40 (20%) of cases, half of which were malignant. • Breast MRI in patients with an implantable loop recorder should be performed when indicated, taking into consideration typical associated artifacts.
Keywords: Artifacts; Breast neoplasms; Magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Society of Radiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safe scanning, but frequent artifacts mimicking bradycardia and tachycardia during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with an implantable loop recorder (ILR).Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005 Oct;10(4):404-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2005.00056.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005. PMID: 16255749 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of magnetic resonance imaging in patients with an implantable loop recorder.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008 Mar;31(3):333-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.00994.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18307629
-
Placement of Reveal LINQ Device in the Left Anterior Axillary Position.Pediatr Cardiol. 2020 Jan;41(1):181-185. doi: 10.1007/s00246-019-02242-9. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Pediatr Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31745583
-
Multimodality imaging in patients with implantable loop recorders: Tips and tricks.Hellenic J Cardiol. 2024 May-Jun;77:93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2023.12.001. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38096953 Review.
-
The implantable loop recorder-an important addition to the armentarium in the management of unexplained syncope.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2012 Mar;41(3):115-24. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2012. PMID: 22538738 Review.
Cited by
-
Axillary Lymph Nodes T2 Signal Intensity Characterization in MRI of Patients With Mucinous Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study.J Breast Imaging. 2025 Mar 18;7(2):187-195. doi: 10.1093/jbi/wbae078. J Breast Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39657258
-
Asymmetric background parenchymal enhancement on contrast-enhanced mammography: associated factors, diagnostic workup, and clinical outcome.Eur Radiol. 2025 Feb;35(2):712-722. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10856-8. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39080066
References
-
- Mayo RC, Leung J (2017) Novel Wireless Cardiac Monitor Located in the Breast: Imaging Appearance and Function. Breast J. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

