Prevalence of dynapenia and overlap with disability, depression, and executive dysfunction
- PMID: 37556665
- PMCID: PMC10355316
- DOI: 10.11606/s1518-8787.2023057004580
Prevalence of dynapenia and overlap with disability, depression, and executive dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate handgrip strength and dynapenia prevalence among older adults stratified by Brazilian macroregions. Additionally, we aim to evaluate the overlap between dynapenia and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) disability, depression, and executive dysfunction on a national basis and by each Brazilian macroregion.
Methods: This cross-sectional analysis was based on data from the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Aging (ELSI-Brazil). A multistage cluster sample design was used, with a representative population-based study of non-institutionalized community-dwelling Brazilians aged ≥ 50 years from 70 municipalities across all five macroregions of the country. The outcome variable was dynapenia. Covariables were IADL disability, depression, and executive dysfunction. The Brazilian macroregions were used for stratification. In addition, the following additional variables were included: age group, gender, education level, macroregions (North, Northeast, Southeast, South, and Midwest), self-reported health, multimorbidity, and falls.
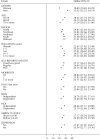
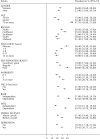
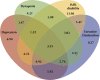
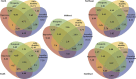
Results: A total of 8,849 (94%) of the sample provided complete information for the handgrip strength assessment and were included in this analysis. Dynapenia prevalence was higher in North and Northeast regions (28.5% and 35.1%, respectively). We identified statistically significant differences between different macroregions for dynapenia, IADL disability, and verbal fluency, with worse values in the North and Northeast regions. In the North and Northeast macroregions, nearly half of the subjects that presented executive dysfunction and IADL disability also had dynapenia. There was a more significant overlap in the prevalence of all four conditions in the North and Northeast regions (4.8% and 5.5%, respectively), whereas the overlap was smaller in the South (2.3%). There was also a smaller overlap in the prevalence of dynapenia and depression in the South (5.8%) compared with other macroregions.
Conclusions: Macroregions in Brazil exhibit marked differences in the prevalence of dynapenia and in its overlap with IADL disability, depression, and executive dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- 2. Rijk JM, Roos PR, Deckx L, van den Akker M, Buntinx F. Prognostic value of handgrip strength in people aged 60 years and older: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016 Jan;16(1):5-20. 10.1111/ggi.12508 - DOI - PubMed
- Rijk JM, Roos PR, Deckx L, van den Akker M, Buntinx F. Prognostic value of handgrip strength in people aged 60 years and older: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2016 Jan;16(1):5–20. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12508. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 3. Montes MC, Bortolotto CC, Tomasi E, Gonzalez MC, Barbosa-Silva TG, Domingues MR, et al. Strength and multimorbidity among community-dwelling elderly from southern Brazil. Nutrition. 2020 Mar;71:110636. 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110636 - DOI - PubMed
- Montes MC, Bortolotto CC, Tomasi E, Gonzalez MC, Barbosa-Silva TG, Domingues MR, et al. Strength and multimorbidity among community-dwelling elderly from southern Brazil. 110636Nutrition. 2020 Mar;71 doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110636. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 4. Noh HM, Park YS. Handgrip strength, dynapenia, and mental health in older Koreans. Sci Rep. 2020 Mar;10(1):4004. 10.1038/s41598-020-60835-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Noh HM, Park YS. Handgrip strength, dynapenia, and mental health in older Koreans. 4004Sci Rep. 2020 Mar;10(1) doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60835-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- 5. Arrieta H, Rezola-Pardo C, Echeverria I, Iturburu M, Gil SM, Yanguas JJ, et al. Physical activity and fitness are associated with verbal memory, quality of life and depression among nursing home residents: preliminary data of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2018 Mar;18(1):80. 10.1186/s12877-018-0770-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Arrieta H, Rezola-Pardo C, Echeverria I, Iturburu M, Gil SM, Yanguas JJ, et al. Physical activity and fitness are associated with verbal memory, quality of life and depression among nursing home residents: preliminary data of a randomized controlled trial. 80BMC Geriatr. 2018 Mar;18(1) doi: 10.1186/s12877-018-0770-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

