Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes (HUCMSC-exos) recovery soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1)-induced endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia
- PMID: 37559150
- PMCID: PMC10413730
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01182-8
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes (HUCMSC-exos) recovery soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1)-induced endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia
Abstract
Background: Preeclampsia is a unique multisystem disorder that affects 5-8% of pregnancies. A high level of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) is a hallmark of preeclampsia that causes endothelial dysfunction. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been indicated to improve endothelial performances by transporting signals to target cells. We hypothesized that exosomes derived from MSCs have potential effects against preeclampsia.
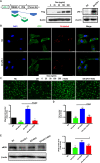
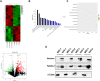
Methods: We collected human umbilical cord MSC-derived exosomes (HUCMSC-exos) by ultracentrifugation. The size and morphology of the exosomes were examined using a transmission electron microscope and nanoparticle tracking analysis. Pregnant mice were injected with murine sFlt-1 adenovirus to build the preeclampsia-like mouse model and then treated with HUCMSC-exos. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were infected with lentiviruses expressing tet-on-sFlt-1 to obtain cells overexpressing sFlt-1. Cell proliferation and migration assays were used to measure the endothelial functions. The exosomes enriched proteins underlying mechanisms were explored by proteomic analysis.
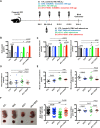
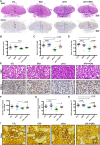
Results: In the current study, we successfully collected the cup-shaped HUCMSC-exos with diameters of 30-150 nm. In the sFlt-1-induced preeclampsia mouse model, HUCMSC-exos exhibited beneficial effects on adverse birth events by decreasing blood pressure and improving fetal birth weight. In addition, preeclamptic dams that were injected with HUCMSC-exos had rebuilt dense placental vascular networks. Furthermore, we observed that HUCMSC-exos partially rescued sFlt-1-induced HUVECs dysfunction in vitro. Proteomics analysis of HUCMSC-exos displayed functional enrichment in biological processes related to vesicle-mediated transport, cell communication, cell migration, and angiogenesis.
Conclusion: We propose that exosomes derived from HUCMSCs contain abundant Versican and play beneficial roles in the birth outcomes of sFlt-1-induced preeclamptic mice by promoting angiogenesis.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Exosomes; Mesenchymal stem cell; Preeclampsia; Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1/sFlt-1.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Souza JP, Gülmezoglu AM, Vogel J, Carroli G, Lumbiganon P, Qureshi Z, et al. Moving beyond essential interventions for reduction of maternal mortality (the WHO Multicountry Survey on Maternal and Newborn Health): a cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2013;381(9879):1747–1755. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60686-8. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

