Aumolertinib in NSCLC with leptomeningeal involvement, harbouring concurrent EGFR exon 19 deletion and TP53 comutation: a case report
- PMID: 37559636
- PMCID: PMC10407486
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-23-841
Aumolertinib in NSCLC with leptomeningeal involvement, harbouring concurrent EGFR exon 19 deletion and TP53 comutation: a case report
Abstract
Background: Aumolertinib (HS-10296), a 3rd-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), has been shown to have efficacy in treating tumors harboring EGFR sensitive mutations: EGFR in-frame deletions or insertions within exon 19 deletion (19Del) and the exon 21 L858R mutation and EGFR T790M resistance mutation. Research has shown that tumor protein p53 (TP53) mutations and leptomeningeal metastases (LM) are associated with reduced responsiveness and a poor prognosis in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have received targeted therapy with EGFR-TKIs. The TP53 mutation is a common concomitant mutation of EGFR amplification in solid tumors. First-line aumolertinib treatment is effective in EGFR concurrent mutated NSCLC, however, the efficacy and survival outcomes in these patients with leptomeningeal metastasis remain unknown.
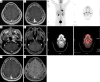
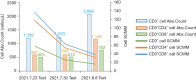
Case description: We retrospectively examined the data of a lung adenocarcinoma patient, 51 years old, male, multi-mutations of EGFR and TP53, who received 1st-line treatment with a 1st-generation TKI followed by 2nd-line treatment with aumolertinib. Before the 1st-line treatment, the patient underwent a lung biopsy to examine the 520 genes of all cancers using illumia high-throughput sequencing. The sequencing results showed that the patient had the EGFR 19del (p.Leu747_Thr751del)/TP53 (p.lys120fs)/EGFR amplified multiple mutation with a low tumor mutational burden. The patient was treated with gefitinib and achieved progression-free survival (PFS) for 10 months until secondary malignancy of the lymph nodes. The first-generation TKI combined with chemotherapy was applied and then the patient was diagnosed with leptomeningeal metastases. Subsequently, the patient was treated with aumolertinib for 12 months without disease progression. The efficacy evaluation was partial response (PR) with grade 2 rash. Adenocarcinoma cells were found in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF-derived circulating tumor deoxyribonucleic acid was detected using the target area probe capture and 2nd-generation high-throughput sequencing technology. The CSF gene detection showed the EGFR p. L747_T751 del, TP53 p. K120fs and EGFR amplification mutations.
Conclusions: This is the first reported case in which aumolertinib was used to treat a patient with the multi-mutations of EGFR 19Del, TP53, and EGFR amplification and leptomeningeal metastases. The findings suggested that almonertinib may result in long-period clinical improvement and tolerable safety in concurrent mutated LM NSCLC.
Keywords: Aumolertinib; case report; co-mutation; leptomeningeal metastases.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-23-841/coif). HZ is employed by Hansoh Health Technology Co., Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
