Genetic ablation of ketohexokinase C isoform impairs pancreatic cancer development
- PMID: 37559908
- PMCID: PMC10407955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107368
Genetic ablation of ketohexokinase C isoform impairs pancreatic cancer development
Abstract
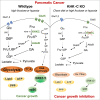
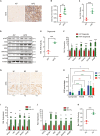
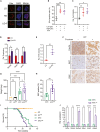
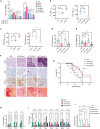
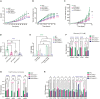
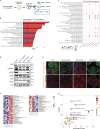
Although dietary fructose is associated with an elevated risk for pancreatic cancer, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we report that ketohexokinase (KHK), the rate-limiting enzyme of fructose metabolism, is a driver of PDAC development. We demonstrate that fructose triggers KHK and induces fructolytic gene expression in mouse and human PDAC. Genetic inactivation of KhkC enhances the survival of KPC-driven PDAC even in the absence of high fructose diet. Furthermore, it decreases the viability, migratory capability, and growth of KPC cells in a cell autonomous manner. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that genetic ablation of KHKC strongly impairs the activation of KRAS-MAPK pathway and of rpS6, a downstream target of mTORC signaling. Moreover, overexpression of KHKC in KPC cells enhances the downstream KRAS pathway and cell viability. Our data provide new insights into the role of KHK in PDAC progression and imply that inhibiting KHK could have profound implications for pancreatic cancer therapy.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Biological sciences; Cancer systems biology; Natural sciences; Systems biology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare no conflict of interest relating to this study.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

