High miR-200c expression is associated with suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition, TGF-β signaling and better survival despite enhanced cell proliferation in gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 37560006
- PMCID: PMC10408478
High miR-200c expression is associated with suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition, TGF-β signaling and better survival despite enhanced cell proliferation in gastric cancer patients
Abstract
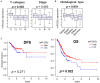
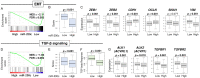
MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that epigenetically regulate gene expression. MiR-200c is a known tumor suppressive microRNA found in many types of cancer, and its high expression has been associated with improved prognosis. However, the association between miR-200c expression and its clinical relevance in gastric cancer (GC) patients remains controversial. Here, we hypothesized that gastric cancer patients with high miR-200c gene expression translated to better overall survival. A total of 372 GC patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) were analyzed. The top three quartiles were defined as a high miR-200c expression group. High miR-200c expression was associated with decreased invasion, favorable histological type, and improved overall survival in gastric cancer patients. Unexpectedly, high miR-200c expression GC was also associated with enhanced cell proliferation, shown by MKi67 expression, proliferation score, and enrichment of Hallmark cell proliferation-related gene sets (E2F targets, G2M checkpoints, MYC targets v1 and v2) by gene set enrichment assay (GSEA). High miR-200c GC was also associated with a high mutation rate and homologous recombination deficiency. Despite the association with elevated neoantigens, high miR-200c GC was associated with significantly low infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells, decreased immune response, and with suppressed IL2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ pathways. On the other hand, GC with low miR-200c expression significantly enriched hypoxia, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and TGF-β signaling gene sets, all of which promote cancer progression and metastasis in GSEA. In conclusion, patients with high miR-200c expression GC had better survival despite association with aggressive tumor biology, such as high mutation rates, cell proliferation, and low cancer immunity. Given that low miR-200c GC was associated with hypoxia, angiogenesis, EMT and TGF-β signaling, we cannot help but speculate that the difference in survival by miR-200c expression may be at least partly due to the association between low miR-200c expression and aggressive biology.
Keywords: EMT; Gastric cancer; angiogenesis; prognosis; signaling.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

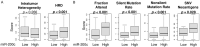


References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Duan Y, Wu C, Peng W, Chen W, Wang L, Deng Z. MiR-200c regulates invasion, proliferation and EMT of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells by targeting parathyroid hormone like hormone. Growth Factors. 2022;40:175–185. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
