Anti-cerebral ischemic neuronal injury mechanism of Zhenlong Xingnao capsules: role of the Notch/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 37560215
- PMCID: PMC10408513
Anti-cerebral ischemic neuronal injury mechanism of Zhenlong Xingnao capsules: role of the Notch/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the anti-cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI) effect and mechanism of Zhenlong Xingnao capsules based on Notch/NF-κB signaling pathway.
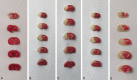
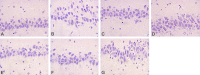
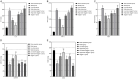
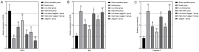
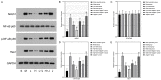
Methods: The rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was established using the Longa suture occlusion method, and 70 rats were divided into sham-operated, model, low dose Zhenlong Xingnao capsule group (125 mg/kg Zhenlong Xingnao capsule solution) and high dose Zhenlong Xingnao capsule group (250 mg/kg Zhenlong Xingnao capsule solution), low dose Zhenlong Xingnao capsule + neurogenic site notch homologous protein 1 (Notch1) antibody (Jagged1 group, 125 mg/kg capsule solution + 25 mg/kg Jagged1 solution), high dose Zhenlong Xingnao capsule + Jagged1 group (250 mg/kg capsule solution + 25 mg/kg Jagged1 solution), and Jagged1 group (25 mg/kg Jagged1 solution). The learning and memory abilities (behavioral score, spontaneous movement, and rotarod test), neurological function score, inflammatory factors and oxidative stress levels [interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), superoxide dismutase (SOD)] in hippocampal tissue, and Bcl-2, Bax, and Caspase-3 mRNA levels were measured by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and Notch1/NF-κB signaling pathway-related protein expression was assessed by Western blot.
Results: The low and high dose interventions of Zhenlong Xingnao capsules significantly improved the learning and memory abilities of MCAO rats, reduced the neurological impairment scores, improved the levels of IL-6, TNF-α, MDA, GSH-Px, SOD, and inhibited the expression levels of Notch1, p-NF-κB p65, and Hes-1 proteins. However, the protective effect of Zhenlong Xingnao capsules on neurons in rat brain tissue could be reduced after treatment with Jagged1.
Conclusions: Zhenlong Xingnao capsules can promote neuronal repair during ischemia-reperfusion, and its mechanism may be related to inhibiting the activation of Notch/NF-κB signaling pathway and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress response.
Keywords: Notch; Zhenlong Xingnao capsules; inflammation; ischemia-reperfusion injury; oxidative stress.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Chuanzhi Tongluo Capsules antagonizes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jun;47(12):3386-3391. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211117.706. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35851133 Chinese.
-
Neuroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Zhenlong Xingnao Capsule in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of Hypoxia.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 26;10:1096. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01096. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31611791 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effect and immune mechanism of berberine on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Nov;36(6):656-661. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6001.2020.137. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33719277 Chinese.
-
Preactivation of Notch1 in remote ischemic preconditioning reduces cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through crosstalk with the NF-κB pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Sep 16;16(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1570-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31526384 Free PMC article.
-
Clematichinenoside Facilitates Recovery of Neurological and Motor Function in Rats after Cerebral Ischemic Injury through Inhibiting Notch/NF-κB Pathway.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Nov;28(11):104288. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 31395423
Cited by
-
Agrimonolide mitigated DSS-induced colitis by modulating the balance between Treg and Th17 cells through the suppression of the Notch and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33803. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33803. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Y, Yi M, Wang D, Zhang Q, Yang L, Yang C. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress to affect cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through targeting miR-30b/GRP78. Inflammation. 2020;43:2264–2275. - PubMed
-
- Fangma Y, Zhou H, Shao C, Yu L, Yang J, Wan H, He Y. Hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating oxidative stress and apoptosis via the silent information regulator 1 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:739864. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hong Q, Ye J, Wang X, Zhang C. The mechanism of gastrodin participating in improving the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through Notch 1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2021;11:271–275.
-
- Hou J, Li H, Xue C, Ma J. Lidocaine relieves spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury via long non-coding RNA MIAT-mediated Notch1 downregulation. J Biochem. 2022;171:411–420. - PubMed
-
- Tang D, Liu X, Chen J. Mitoquinone intravitreal injection ameliorates retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats involving SIRT1/Notch1/NADPH axis. Drug Dev Res. 2022;83:800–810. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
