Evaluation of Current Literature on Complications Secondary to Lip Augmentation Following Dermal Filler Injection
- PMID: 37560504
- PMCID: PMC10409513
Evaluation of Current Literature on Complications Secondary to Lip Augmentation Following Dermal Filler Injection
Abstract
Background: The current popularity of dermal filler treatments as an alternative to invasive surgical cosmetic procedures has led to an increase in filler-related complications. Lip filler treatments are among the most sought-after injectable treatments and a thorough understanding of the complications of lip filler injections, and their management, is essential for any practitioner.
Objective: The aim of this review is to evaluate the current literature on complications secondary to lip augmentation following non-permanent dermal fillers.
Methods: A thorough MEDLINE literature search of keywords, including lip filler, augmentation, injection, filler, dermal filler, and complications, was completed to collate cases of complications secondary to lip filler injections.
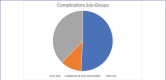
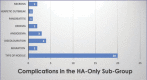
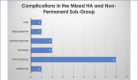
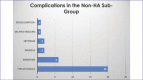
Results: Of our 53 cases that were studied, 82 complications were reported. Our review and evaluation of these cases showed that HA filler was most commonly used in this region, alone or in combination with other soft tissue fillers. The majority of complications resulted from HA involvement, however its frequency of use likely accounts for this. Across all three filler types, the most common complication was nodule formation. Other complications, such as migration, discoloration and herpetic outbreaks, have been linked with filler placement in the lip area.
Conclusion: It is clear that filler treatments carry a variety of risks, thus it becomes of utmost importance to truly understand the product we are working with, its properties, its associated risks, and how to manage those risks. We have to ensure that patients are adequately informed about the risks associated, and understand what those risks entail.
Keywords: Hyaluronic acid; complicatios; cosmetic complications; dermal filler; lip filler; lip filler complications.
Copyright © 2023. Matrix Medical Communications. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES: The authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lip Filler Versus "Lip Flip": Longitudinal Public Interest and a Brief Review of Literature.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Feb;24(2):e70048. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70048. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39936357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aesthetic lip filler augmentation is not free of adverse reactions: lack of evidence-based practice from a systematic review.Front Oral Health. 2024 Oct 17;5:1495012. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1495012. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39483115 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Granulomas as a Complication Secondary to Lip Augmentation with Dermal Fillers: A Systematic Review.Surg J (N Y). 2022 Mar 3;8(1):e69-e79. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1743524. eCollection 2022 Jan. Surg J (N Y). 2022. PMID: 35252562 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed Complications following Dermal Filler for Tear Trough Augmentation: A Systematic Review.Facial Plast Surg. 2022 Jun;38(3):250-259. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1736390. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Facial Plast Surg. 2022. PMID: 34666405
-
Case Series and Review on Managing Abscesses Secondary to Hyaluronic Acid Soft Tissue Fillers with Recommended Management Guidelines.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020 Nov;13(11):37-43. Epub 2020 Nov 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33282102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lip Filler Versus "Lip Flip": Longitudinal Public Interest and a Brief Review of Literature.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Feb;24(2):e70048. doi: 10.1111/jocd.70048. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39936357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Redefinition and Volumization of the Lip Area with Hyaluronic Acid: A Case Series.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 25;13(19):5705. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195705. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407764 Free PMC article.
-
Aesthetic lip filler augmentation is not free of adverse reactions: lack of evidence-based practice from a systematic review.Front Oral Health. 2024 Oct 17;5:1495012. doi: 10.3389/froh.2024.1495012. eCollection 2024. Front Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39483115 Free PMC article.
-
Decades of Scientific Data and Global Media Reporting on Complications in Non-surgical Aesthetic Treatments for a Transparent Safety Profile: Kissing Snow White Awake.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jul 1. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05007-3. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40593115
-
Good scientific practice of using worldwide post-marketing surveillance data to ensure safety with HAALI BDDE cross-linked hyaluronic acid fillers.Drugs Context. 2024 Dec 18;13:2024-10-6. doi: 10.7573/dic.2024-10-6. eCollection 2024. Drugs Context. 2024. PMID: 39717059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ISAPS. ISAPS internationals survey on aesthetic/cosmetic procedures performed in 2017. 2017.
-
- Keogh B Review of the Regulation of Cosmetic Interventions. 2013. Department of Health Publication.
-
- de Maio M. The minimal approach: an innovation in facial cosmetic procedures. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2004;28(5):295–300. - PubMed
-
- Modarressi A, Nizet C, Lombardi T. Granulomas and nongranulomatous nodules after filler injection: Different complications require different treatments. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 2020;73(11):2010–2015. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
