Harnessing developmental cues for cardiomyocyte production
- PMID: 37560977
- PMCID: PMC10445742
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.201483
Harnessing developmental cues for cardiomyocyte production
Abstract
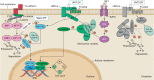
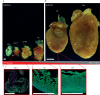
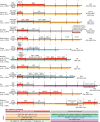
Developmental research has attempted to untangle the exact signals that control heart growth and size, with knockout studies in mice identifying pivotal roles for Wnt and Hippo signaling during embryonic and fetal heart growth. Despite this improved understanding, no clinically relevant therapies are yet available to compensate for the loss of functional adult myocardium and the absence of mature cardiomyocyte renewal that underlies cardiomyopathies of multiple origins. It remains of great interest to understand which mechanisms are responsible for the decline in proliferation in adult hearts and to elucidate new strategies for the stimulation of cardiac regeneration. Multiple signaling pathways have been identified that regulate the proliferation of cardiomyocytes in the embryonic heart and appear to be upregulated in postnatal injured hearts. In this Review, we highlight the interaction of signaling pathways in heart development and discuss how this knowledge has been translated into current technologies for cardiomyocyte production.
Keywords: Cardiomyocyte production; Cardiomyocyte proliferation; Cardiomyocyte self-renewal; Embryonic growth pathways; Fetal gene program; Heart regeneration; Hippo signaling; Wnt signaling; hiPSC-CM.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests J.W.B. and S.M.W. hold a patent on the expansion of hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Abecasis, B., Aguiar, T., Arnault, É., Costa, R., Gomes-Alves, P., Aspegren, A., Serra, M. and Alves, P. M. (2017). Expansion of 3D human induced pluripotent stem cell aggregates in bioreactors: bioprocess intensification and scaling-up approaches. J. Biotechnol. 246, 81-93. 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.01.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alam, P., Haile, B., Arif, M., Pandey, R., Rokvic, M., Nieman, M., Maliken, B. D., Paul, A., Wang, Y. G., Sadayappan, S.et al. (2019). Inhibition of senescence-associated genes Rb1 and Meis2 in adult cardiomyocytes results in cell cycle reentry and cardiac repair post-myocardial infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 8, e012089. 10.1161/JAHA.119.012089 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

