Grating-incoupled waveguide-enhanced Raman sensor
- PMID: 37561713
- PMCID: PMC10414634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284058
Grating-incoupled waveguide-enhanced Raman sensor
Abstract
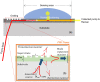
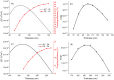
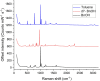
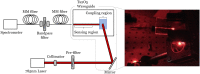
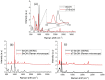
We report a waveguide-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (WERS) platform with alignment-tolerant under-chip grating input coupling. The demonstration is based on a 100-nm thick planar (slab) tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) waveguide and the use of benzyl alcohol (BnOH) and its deuterated form (d7- BnOH) as reference analytes. The use of grating couplers simplifies the WERS system by providing improved translational alignment tolerance, important for disposable chips, as well as contributing to improved Raman conversion efficiency. The use of non-volatile, non-toxic BnOH and d7-BnOH as chemical analytes results in easily observable shifts in the Raman vibration lines between the two forms, making them good candidates for calibrating Raman systems. The design and fabrication of the waveguide and grating couplers are described, and a discussion of further potential improvements in performance is presented.
Copyright: © 2023 Ettabib et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Evans C. C., Liu C., and Suntivich J., “TiO2 nanophotonic sensors for efficient integrated evanescent Raman spectroscopy,” ACS Photon. 3, 1662–1669 (2016).
-
- Michon J., Kita D., and Hu J., “Sensitivity comparison of free-space and waveguide Raman for bulk sensing,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 37, 2012–2020 (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

