Assessment of the relationship between the level of patient knowledge on warfarin therapy and the quality of oral anticoagulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37561771
- PMCID: PMC10414645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289836
Assessment of the relationship between the level of patient knowledge on warfarin therapy and the quality of oral anticoagulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
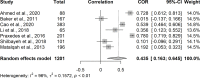
The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between the level of patient knowledge on warfarin therapy and the quality of oral anticoagulation. This is a systematic review and meta-analysis written on the basis of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline. Searches at MEDLINE, EMBASE, Scopus and LILACS electronic databases were carried out on February 13, 2023, using the descriptors "Patient Medication Knowledge", "Patient Education as Topic", "Health Education", "Patient Education" and Warfarin. The steps of selection, data extraction and quality analysis of articles were performed independently by two reviewers. The analysis was performed considering patient knowledge as a possible modifier of time in therapeutic range (TTR). The meta-analysis included studies that reported the correlation coefficient (Pearson or Spearman) between patient knowledge and TTR. A subgroup analysis was performed according to questionnaires employed to measure patient knowledge. Twelve studies were selected with an overall sample size of 7634 participants and mean age 58.2 (standard deviation (SD)±12,8) years. Eleven (92.0%) cross-sectional studies. The mean TTR was 57.8% (SD±11,3%) and the average level of knowledge was 60.4%. The meta-analysis indicated that patient level of knowledge on warfarin therapy was moderately associated with TTR (rs = 0.435; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.163-0.645; I2 = 96%). Subgroup analysis indicated association between knowledge level and TTR in studies employing the OAK test (rs = 0.617; 95% CI = 0.192-0.847; I2 = 97%) and the AKA (rs = 0.269; 95% CI = 0.002 to 0.501; I2 = 94%). However, the subgroup analysis presented no significant difference between them (p = 0.14). The meta-regression showed a non-significant negative effect of age on the correlation (estimate = -0.028, 95% CI = -0.073 to 0.016, p = 0.207). No publication bias was noted (p = 0.881). To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis gathering evidence about the relationship between the level of patient knowledge on oral anticoagulation with warfarin and TTR. The implementation of structured and patient-centered educational interventions is essential to effectively increase the level of patient knowledge and, thus, to improve the quality and safety of warfarin therapy. Systematic review registration number: PROSPERO CRD42023398030.
Copyright: © 2023 Praxedes et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Praxedes MFS, Martins MAP, Mourão AOM, Gomes KB, Reis EA, Souza RP, et al.. Non-genetic factors and polymorphisms in genes CYP2C9 and VKORC1: predictive algorithms for TTR in Brazilian patients on warfarin. European journal of clinical pharmacology. 2020;76(2):199–209. doi: 10.1007/s00228-019-02772-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park YK, Lee MJ, Kim JH, Lee JS, Park RW, Kim GM, et al.. Genetic and Non-Genetic Factors Affecting the Quality of Anticoagulation Control and Vascular Events in Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases: the official journal of National Stroke Association. 2017;26(6):1383–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.02.022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

