CT radiomics for prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37562218
- PMCID: PMC10432601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100264
CT radiomics for prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
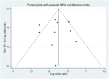
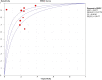
The power of computed tomography (CT) radiomics for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion (MVI) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) demonstrated in current research is variable. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to evaluate the value of CT radiomics for MVI prediction in HCC, and to investigate the methodologic quality in the workflow of radiomics research. Databases of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were systematically searched. The methodologic quality of included studies was assessed. Validation data from studies with Transparent Reporting of a Multivariable Prediction Model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD) statement type 2a or above were extracted for meta-analysis. Eleven studies were included, among which nine were eligible for meta-analysis. Radiomics quality scores of the enrolled eleven studies varied from 6 to 17, accounting for 16.7%-47.2% of the total points, with an average score of 14. Pooled sensitivity, specificity, and Area Under the summary receiver operator Characteristic Curve (AUC) were 0.82 (95% CI 0.77-0.86), 0.79 (95% CI 0.75-0.83), and 0.87 (95% CI 0.84-0.91) for the predictive performance of CT radiomics, respectively. Meta-regression and subgroup analyses showed radiomics model based on 3D tumor segmentation, and deep learning model achieved superior performances compared to 2D segmentation and non-deep learning model, respectively (AUC: 0.93 vs. 0.83, and 0.97 vs. 0.83, respectively). This study proves that CT radiomics could predict MVI in HCC. The heterogeneity of the included studies precludes a definition of the role of CT radiomics in predicting MVI, but methodology warrants uniformization in the radiology community regarding radiomics in HCC.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Meta-analysis; Microvascular invasion; Radiomics; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2023 HCFMUSP. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of MRI Radiomics for Predicting Microvascular Invasion in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Med Imaging. 2024;20:e15734056256824. doi: 10.2174/0115734056256824231204073534. Curr Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38389371
-
The Diagnostic Accuracy Between Radiomics Model and Non-radiomics Model for Preoperative of Microvascular Invasion of Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2024 Nov;31(11):4419-4433. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.04.003. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38664142
-
Diagnostic performance of FDG PET/CT radiomics in predicting microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma compared to conventional metabolic parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Nucl Med. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s12149-025-02075-y. Online ahead of print. Ann Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40581726
-
Using deep learning to predict microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma based on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI combined with clinical parameters.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Dec;147(12):3757-3767. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03617-3. Epub 2021 Apr 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33839938 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-Based Radiomics Methods for Predicting Ki-67 Expression in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2024 Mar;31(3):763-787. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2023.10.010. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37925343
Cited by
-
Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with microvascular invasion (2024 edition).Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2025 Apr 1;14(2):246-266. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-24-359. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40342785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrast-enhanced CT radiomics features to preoperatively identify differences between tumor and proximal tumor-adjacent and tumor-distant tissues of resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Imaging. 2024 Jan 19;24(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00656-0. Cancer Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38243339 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Pre-Transplant Risk Score (LT-MVI Score) to Predict Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Candidates for Liver Transplantation.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 24;17(9):1418. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091418. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361345 Free PMC article.
-
Current Advances in Classification, Prediction and Management of Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Aug;29(15):e70746. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70746. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40736417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Application Status of Radiomics-Based Machine Learning in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 5;27:e69906. doi: 10.2196/69906. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40323647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forner A., Reig M., Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2019;391(10127):1301–1314. - PubMed
-
- Marrero J.A., Kulik L.M., Sirlin C.B., Zhu A.X., Finn R.S., Abecassis M.M., et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the. Hepatology. 2018;68(2):723–750. - PubMed
-
- Erstad D.J., Tanabe K.K. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(5):1474–1493. - PubMed
-
- Reginelli A., Vacca G., Segreto T., Picascia R., Clemente A., Urraro1 F., et al. Can microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma be predicted by diagnostic imaging? A critical review. Future Oncol. 2018;14(28):2985–2994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

