Social Buffering Effects during Craft Activities in Parallel Group Session Revealed by EEG Analysis and Parasympathetic Activity
- PMID: 37562371
- PMCID: PMC10614439
- DOI: 10.1159/000531005
Social Buffering Effects during Craft Activities in Parallel Group Session Revealed by EEG Analysis and Parasympathetic Activity
Abstract
Introduction: The therapeutic structure of occupational therapy (OT) includes groups. Although the presence of others is expected to be relaxing due to the social buffering effect and the tend and befriend theory, it has not been sufficiently validated in accordance with the therapeutic structure of OT. The aim of this study was to investigate the electrophysiological evidence for the effectiveness of parallel groups and states of concentration on craft activities used in OT.
Methods: Thirty healthy young adults were used as controls to measure EEG and autonomic activity during craft activities in three conditions: alone, parallel, and nonparallel. EEG was analyzed using exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography, and autonomic activity was analyzed using Lorenz plot analysis.
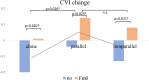
Results: Parasympathetic activity was significantly higher in the parallel condition than in the alone condition. A significant negative correlation was found between current source density and parasympathetic activity in the region centered on the right insular cortex in the α1 band, and functional connectivity in regions including the anterior cingulate cortex and insular cortex was associated with autonomic activity.
Conclusion: Craft activities that occurred during frontal midline theta rhythm also increased parasympathetic activity. The results suggest that the parallel groups used in OT and the intensive state of craft activities induce a social buffering effect that increases parasympathetic activity despite the absence of physical contact or social support. This provides evidence for the effectiveness of the therapeutic structure of occupational activities and groups in OT.
Keywords: Craft activity; EEG; Exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography; Frontal midline theta rhythm; Lorenz plot; Occupational therapy; Parallel group; Parasympathetic activity.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Psychophysiological and interpersonal effects of parallel group crafting: a multimodal study using EEG and ECG.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68980-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095523 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Electroencephalography and Cardiac Autonomic Function During Craft Activities: Experimental Evidence for the Effectiveness of Occupational Therapy.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Dec 11;14:621826. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.621826. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33424571 Free PMC article.
-
Frontal midline theta rhythm is correlated with cardiac autonomic activities during the performance of an attention demanding meditation procedure.Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2001 Apr;11(2):281-7. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6410(00)00086-0. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11275489
-
Interhemispheric Asymmetries and Theta Activity in the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex as EEG Signature of HIV-Related Depression: Gender Matters.Clin EEG Neurosci. 2016 Apr;47(2):96-104. doi: 10.1177/1550059414563306. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Clin EEG Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 25568149
-
Frontal theta and posterior alpha in resting EEG: A critical examination of convergent and discriminant validity.Psychophysiology. 2020 Feb;57(2):e13483. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13483. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Psychophysiology. 2020. PMID: 31578740 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Altruism Enhances Frontal Alpha Asymmetry and Reduces Sympathetic Activity: A Multimodal EEG-ECG Study With Implications for Therapeutic Interventions.Brain Behav. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70747. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70747. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40842172 Free PMC article.
-
Neurophysiological effects of altruistically motivated craft activities in occupational therapy: A pilot study using frontal EEG and heart rate variability analysis.Hong Kong J Occup Ther. 2025 Feb 17;38(1):15-23. doi: 10.1177/15691861251319466. eCollection 2025 Jun. Hong Kong J Occup Ther. 2025. PMID: 39975471 Free PMC article.
-
Psychophysiological and interpersonal effects of parallel group crafting: a multimodal study using EEG and ECG.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 2;14(1):17883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68980-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39095523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowman ND, Weber R, Tamborini R, Sherry J. Facilitating game play: how others affect performance at and enjoyment of video games. Media Psychol. 2013 Jan;16(1):39–64. 10.1080/15213269.2012.742360. - DOI
-
- Hoyt CL, Blascovich J, Swinth KR. Social inhibition in immersive virtual environments. Presence. 2003 Apr;12(2):183–95. 10.1162/105474603321640932. - DOI
-
- Kao D. The effects of observation in video games: how remote observation influences player experience, motivation, and behaviour. Behav Inf Technol. 2022 Jul;41(9):1905–27. 10.1080/0144929x.2021.1906321. - DOI

