Generation of precision preclinical cancer models using regulated in vivo base editing
- PMID: 37563300
- PMCID: PMC11295146
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-023-01900-x
Generation of precision preclinical cancer models using regulated in vivo base editing
Abstract
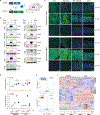
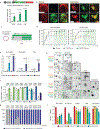
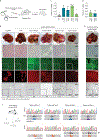
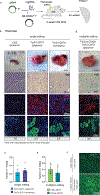
Although single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) make up the majority of cancer-associated genetic changes and have been comprehensively catalogued, little is known about their impact on tumor initiation and progression. To enable the functional interrogation of cancer-associated SNVs, we developed a mouse system for temporal and regulatable in vivo base editing. The inducible base editing (iBE) mouse carries a single expression-optimized cytosine base editor transgene under the control of a tetracycline response element and enables robust, doxycycline-dependent expression across a broad range of tissues in vivo. Combined with plasmid-based or synthetic guide RNAs, iBE drives efficient engineering of individual or multiple SNVs in intestinal, lung and pancreatic organoids. Temporal regulation of base editor activity allows controlled sequential genome editing ex vivo and in vivo, and delivery of sgRNAs directly to target tissues facilitates generation of in situ preclinical cancer models.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
L.E.D. is a scientific advisor and holds equity in Mirimus Inc. L.E.D. has received consulting fees and/or honoraria from Volastra Therapeutics, Revolution Medicines, Repare Therapeutics, Fog Pharma, and Frazier Healthcare Partners. S.W.L is an advisor for and has equity in the following biotechnology companies: ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Faeth Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Geras Bio, Mirimus Inc., PMV Pharmaceuticals, and Constellation Pharmaceuticals. SWL acknowledges receiving funding and research support from Agilent Technologies for the purposes of massively parallel oligo synthesis. K.H., A.P.K, and J.A.W are employees and shareholders of Synthego Corporation.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

