Transmitted/founder SHIV.D replicates in the brain, causes neuropathogenesis, and persists on combination antiretroviral therapy in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 37563642
- PMCID: PMC10413509
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-023-00628-5
Transmitted/founder SHIV.D replicates in the brain, causes neuropathogenesis, and persists on combination antiretroviral therapy in rhesus macaques
Abstract
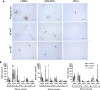
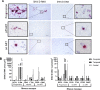
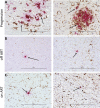
A biologically relevant non-human primate (NHP) model of HIV persistence in the central nervous system (CNS) is necessary. Most current NHP/SIV models of HIV infection fail to recapitulate viral persistence in the CNS without encephalitis or fail to employ viruses that authentically represent the ongoing HIV-1 pandemic. Here, we demonstrate viral replication in the brain and neuropathogenesis after combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) in rhesus macaques (RMs) using novel macrophage-tropic transmitted/founder (TF) simian-human immunodeficiency virus SHIV.D.191,859 (SHIV.D). Quantitative immunohistochemistry (IHC) and DNA/RNAscope in situ hybridization (ISH) were performed on three brain regions from six SHIV.D-infected RMs; two necropsied while viremic, two during analytical treatment interruptions, and two on suppressive ART. We demonstrated myeloid-mediated neuroinflammation, viral replication, and proviral DNA in the brain in all animals. These results demonstrate that TF SHIV.D models native HIV-1 CNS replication, pathogenesis, and persistence on ART in rhesus macaques.
Keywords: HIV; NeuroHIV; Non-human primates; Persistence; SHIV.
© 2023. Diane D. Jeang.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Burdo is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board and holds equity in Excision BioTherapeutics (unrelated to this study). All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Koenig S, Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Canto MCD, Pezeshkpour GH, Yungbluth M, Janotta F, Aksamit A, Martin MA, Fauci AS. Detection of AIDS Virus in Macrophages in Brain tissue from AIDS patients with Encephalopathy. Science; 1986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

