Age- and sex-related trends in body composition among Beijing adults aged 20-60 years: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37563675
- PMCID: PMC10413732
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-16459-0
Age- and sex-related trends in body composition among Beijing adults aged 20-60 years: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Obesity is the most serious global epidemic and body composition is the main indicator to evaluate obesity. This study aimed to investigate the changing trends of body composition by age and gender in Beijing adults aged 20-60 years and explore the distribution of obesity rates in different age groups of both sexes under different evaluation criteria.
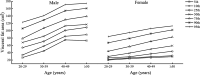
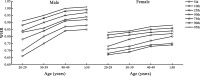
Methods: A total of 24,948 adults aged 20-60 years in Beijing, including 10,225 males and 14,192 females, were included, divided into four age groups (20-29, 30-39, 40-49, and ≥ 50 years) with each decade of age as an age group. Body composition indicators (BMI, fat mass, BF%, muscle mass, visceral fat area, and WHR) were measured in all subjects.
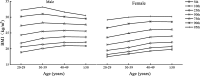
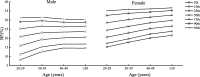
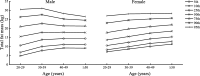
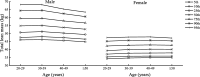
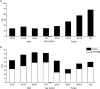
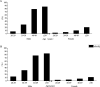
Results: BMI and total fat mass peaked in males aged 40-49 years (BMI = 25.75 kg/m2, total fat mass = 17.70 kg). Female BMI, fat mass and BF% all increased significantly with age (p < 0.01). Total muscle peaked in males aged 30-39 years and decreased significantly thereafter (p < 0.0001). Visceral fat area and WHR increased significantly with age in both sexes (p < 0.0001). Age was significantly positively correlated with BMI, BF%, fat mass, WHR, and visceral fat area in both sexes (p < 0.0001), and age was negatively correlated with muscle mass in males (standard β = - 0.14, p < 0.0001) while positive in female (standard β = 0.05, p < 0.0001). Under the BMI criterion, the obesity rate peaked at 27.33% in males at the age of 20-29 years. Under the BF% criterion, the obesity rate peaked at 17.41% in males at the age of 30-39 years, and increased in females with age. The central obesity rate of both sexes increased with age under the criteria of WHR and visceral fat area.
Conclusion: The results of this study reveal that age- and sex-related patterns of body composition and obesity change among Beijing adults aged 20-60 years may differ across age groups and that such patterns of change should be considered when developing public health strategies.
Keywords: Age; Beijing adults; Body composition; Obesity; Sex.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between Body Mass Index (BMI) and body fat percentage, estimated by bioelectrical impedance, in a group of Sri Lankan adults: a cross sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2013 Sep 3;13:797. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-797. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 24004464 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in overweight or obesity and other anthropometric indices in adults aged 18-60 years in western Saudi Arabia.Ann Saudi Med. 2017 Mar-Apr;37(2):106-113. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2017.106. Ann Saudi Med. 2017. PMID: 28377539 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence Rate of Adult Sarcopenic Obesity and Correlation of Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass Index with Body Mass Index, Percent Body Fat, Waist-Hip Ratio, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Visceral Fat Area.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2023 Feb;21(1):48-56. doi: 10.1089/met.2022.0035. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36318808
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
-
The Obesity Paradox in Cancer-Moving Beyond BMI.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017 Jan;26(1):13-16. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0439. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017. PMID: 28069727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A study on the construction of body fat percentage percentile curve for adults aged 20-79 in China.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 20;13:1598285. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1598285. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40620559 Free PMC article.
-
The Association of Body Mass Index and Adiposity-Estimating Equations with Measures of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nat Sci Sleep. 2025 May 22;17:1003-1019. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S504426. eCollection 2025. Nat Sci Sleep. 2025. PMID: 40432910 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences of visceral fat with cardiac structure and function in type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study.J Diabetes. 2024 Nov;16(11):e70023. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.70023. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39511977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, Mullany EC, Biryukov S, Abbafati C, Abera SF, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384(9945):766–781. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

