The value of lymph nodes ratios in the prognosis of resectable remnant gastric cancer through the retrospective propensity score matching analysis
- PMID: 37563693
- PMCID: PMC10416507
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-023-03137-z
The value of lymph nodes ratios in the prognosis of resectable remnant gastric cancer through the retrospective propensity score matching analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Currently, the characteristics and prognosis of remnant gastric cancer (RGC) are not fully understood yet. The present study aimed to describe the details of clinicopathological features of resectable RGC and investigated the factors affecting survival after the curative operation.
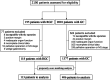
Methods: From Jan. 2006 to Dec. 2015, a total of 118 resectable RGC patients (the RGC group) and 236 age-, sex- and TNM stages-matched resectable gastric cancer (GC) patients (the control group) were recruited retrospectively. Clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival were compared between the two groups.
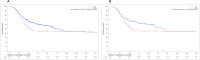
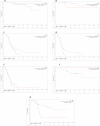
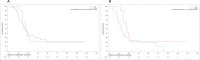
Results: The overall survival rate was 46.61% for RGC patients compared to 55.08% for control groups (P < 0.01), and the mean overall survival time of RGC patients was 40.23 ± 32.27 months, compared to 55.06 ± 34.29 months in the control group (P = 0.023 after matching). The overall survival (OS) of RGC patients with stage IIb was much worse than IIa (P < 0.001) and similar to IIIa (P = 0.463) and IIIb (P = 0.014). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards model analysis revealed that TNM stage (HR: 3.899, P < 0.001) and lymph nodes ratio (LNR) (HR: 2.405, P = 0.028) were independent prognostic significance to OS.
Conclusions: The OS of RGC was much worse than GC with similar TNM stages, and LNR might consider a highly reliable indicator to evaluate the prognostic in RGC.
Keywords: Clinicopathological characteristics; Lymph nodes ratio; Overall survival; Remnant gastric cancer.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different prognostic effect of lymph node metastasis between remnant gastric cancers and primary proximal gastric cancers.J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Oct;28(10):1571-1577. doi: 10.1016/j.gassur.2024.06.026. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 38964532
-
Evaluation of Lymph Node Staging Systems as Independent Prognosticators in Remnant Gastric Cancer Patients with an Insufficient Number of Harvested Lymph Nodes.Ann Surg Oncol. 2021 May;28(5):2866-2876. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-09433-2. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33393020
-
Prognostic significance of metastatic lymph node ratio in patients with gastric cancer after curative gastrectomy: a single-center retrospective study.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul;57(7):832-841. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2022.2036807. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35293268
-
Positive lymph node ratio is an index in predicting prognosis for remnant gastric cancer with insufficient retrieved lymph node in R0 resection.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 21;11(1):2022. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81663-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33479327 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of lymph node ratio for local advanced gastric cancer patients with adjuvant chemoradiotherapy after D2 gastrectomy.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e13079. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013079. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383693 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the predictive performance of three lymph node staging systems for late-onset gastric cancer patients after surgery.Front Surg. 2024 Jun 11;11:1376702. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1376702. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38919979 Free PMC article.
-
Using the geriatric nutritional risk index to predict outcomes in older patients with remnant gastric cancer after gastrectomy: a retrospective multicenter study in Japan.Surg Today. 2024 Nov;54(11):1360-1368. doi: 10.1007/s00595-024-02850-w. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Surg Today. 2024. PMID: 38652300
-
Identification of prognostic signatures in remnant gastric cancer through an interpretable risk model based on machine learning: a multicenter cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 30;24(1):547. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12303-9. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38689252 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori activates SLFN4+MDSCs to accelerate gastric intestinal metaplasia.iScience. 2024 Oct 28;27(11):111255. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111255. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39620128 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphovascular invasion is associated with poor long-term outcomes in patients with pT1N0-3 or pT2-3N0 remnant gastric cancer: a retrospective cohort study.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Apr 5;22(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03371-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38581014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Japanese Gastric Cancer A. Japanese Classification of Gastric Carcinoma - 2nd English Edition. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1(1):10–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

