The Penetration Depth of Resin Infiltration Into Enamel: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37564169
- PMCID: PMC10411299
- DOI: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_36_23
The Penetration Depth of Resin Infiltration Into Enamel: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Aims and objectives: Studies on resin infiltration and its penetration capability are becoming the focus of emerging dentistry. The depth of resin penetration could be a key determining factor in creating a diffusion barrier and in the success of infiltration. The aim of this review article was to evaluate the penetration depth of commercially available resin infiltration in early caries lesions and to identify factors that influence the penetration capability of resin infiltration.
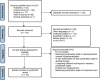
Materials and methods: A literature search was performed in four databases (PubMed, Science Direct, Scopus, and Web of Science) and manual searching from 2009 to December 2022. Eligibility criteria included in vitro studies pertaining to factors affecting the penetration depth of resin infiltration into the enamel. The risk of bias assessment was done by using checklist for reporting in vitro studies (CRIS).
Results: The initial search resulted in a total of 297 studies. Twenty-nine were assessed for eligibility, and 23 were selected in the qualitative synthesis. According to the CRIS guidelines, all of the studies were classified as moderate risk of bias. The penetration of resin infiltration is influenced by the enamel surface treatment with hydrochloric acid, formulations containing triethylene glycol dimethacrylate (TEGDMA), the addition of ethanol, penetration time, duration of penetration time, saliva contamination, caries activity, and type of tooth. The hypermineralized surface layer needs to be removed for better resin perfusion.
Conclusion: The key to optimal resin infiltration depends on the enamel surface treatment with hydrochloric acid and application technique, infiltration duration, formulation of TEGDMA and ethanol in the resin composition, as well as the type and caries activity of involved teeth. Resin infiltration has superior penetrability compared to fissure sealant, casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomplexes, flowable composite, adhesive and fluoride varnish. Resin penetration depth may be a critical factor in forming a diffusion barrier and the effectiveness of infiltration in halting the progression of caries.
Keywords: Adhesive; etching; ethanol; hydrochloric acid; penetration depth; resin infiltration.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[An experimental study on the penetration abilities of resin infiltration into proximal caries lesions in primary molars].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Nov;47(11):684-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2012.11.011. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23302432 Chinese.
-
[A study on the penetration abilities of natural initial caries lesions with resin infiltration].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Oct;30(5):483-6. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23173311 Chinese.
-
In Vitro Effects of Resin Infiltration on Enamel Erosion Inhibition.Oper Dent. 2015 Sep-Oct;40(5):492-502. doi: 10.2341/14-162-L. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Oper Dent. 2015. PMID: 25587972
-
Resin Infiltration Therapy: A micro-invasive treatment approach for white spot lesions.J Dent Hyg. 2021 Dec;95(6):31-35. J Dent Hyg. 2021. PMID: 34949680 Review.
-
Micro-invasive interventions for managing non-cavitated proximal caries of different depths: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2018 Nov;22(8):2675-2684. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2605-9. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Clin Oral Investig. 2018. PMID: 30238416
Cited by
-
In-vitro comparative thermo-chemical aging and penetration analyses of bioactive glass-based dental resin infiltrates.PeerJ. 2025 Jan 28;13:e18831. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18831. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39897486 Free PMC article.
-
Aesthetic impact of resin infiltration and its mechanical effect on ceramic bonding for white spot lesions.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Mar 21;24(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04011-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38515110 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of temperature on the shear bond strength of conventional multi-step and self-adhesive orthodontic adhesive systems: an in-vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05515-3. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 39910542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin GSS, Chan DZK, Lee HY, Low TT, Laer TS, Pillai MPM, et al. Effectiveness of resin infiltration in caries inhibition and aesthetic appearance improvement of white-spot lesions: an umbrella review. J Evid Based Dent Pract. 2022;22:101723. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources