FIBP interacts with transcription factor STAT3 to induce EME1 expression and drive radioresistance in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37564211
- PMCID: PMC10411469
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.83134
FIBP interacts with transcription factor STAT3 to induce EME1 expression and drive radioresistance in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
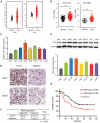
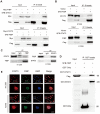
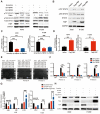
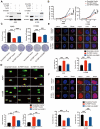
Cancer cells inevitably develop radioresistance during lung adenocarcinoma radiotherapy. However, the mechanisms are incompletely clarified. In this study, we show that FIBP protein expression in lung adenocarcinoma tissues is upregulated and associated with worse overall survival. Functionally, we find that depletion of FIBP inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression and radioresistance in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we uncover that FIBP interacts with STAT3 to enhance its transcriptional activity, thereby inducing the expression of the downstream target gene EME1. Importantly, we demonstrate that the biological effects of FIBP are partially dependent on EME1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Our work reveals that FIBP modulates the STAT3/EME1 axis to drive lung cancer progression and radioresistance, indicating that targeting FIBP may be a novel intervention strategy for lung adenocarcinoma radiotherapy.
Keywords: EME1; FIBP; STAT3; lung adenocarcinoma; radioresistance.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ, Wu Y-L. et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

