Safety and efficacy of intranasal insulin in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37564252
- PMCID: PMC10411979
Safety and efficacy of intranasal insulin in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and aim: We performed this meta-analysis to evaluate the safety and efficacy of intranasal insulin in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients.
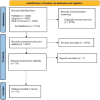
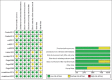
Methods: A literature search was conducted for PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science from inception until August 2022. Documents were screened for qualified articles, and all concerned outcomes were pooled as risk ratios or mean difference (MD) in the meta-analysis models using Review Manager (RevMan version 5.4).
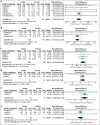
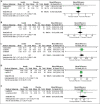
Results: Our results from 12 studies favored intranasal insulin over placebo in terms of Alzheimer Disease's Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog) 20 IU, (MD = -0.13, 95% CI [-0.22, -0.05], P = 0.003). The overall effect did not favor either of the two groups for ADAS-cog 40 IU, memory composite 20 IU and 40 IU, and adverse events (MD = -0.08, 95% CI [-0.16, 0.01], P = 0.08), (MD = 0.65, 95% CI [-0.08, 1.39], P = 0.08), (MD = 0.25, 95% CI [-0.09, 0.6], P = 0.15), and (MD = 1.28, 95% CI [0.75, 2.21], P = 0.36), respectively.
Conclusion: Ultimately, this meta-analysis showed that intranasal insulin in small doses (20 IU) significantly affects patients with AD. Further studies are recommended on reliable insulin delivery devices to increase insulin in the central nervous system.
Relevance for patients: Intranasal insulin has shown promising results in treating patients with AD. The lower doses (20 IU) can play a positive role in improving the disease. As research continues, it is likely that this treatment will become more widely accepted and utilized in clinical practice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; intranasal insulin; mild cognitive impairment.
Copyright: © 2023 Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kazkayasi I, Telli G, Nemutlu E, Uma S. Intranasal Metformin Treatment Ameliorates Cognitive Functions Via Insulin Signaling Pathway in ICV-STZ-induced Mice Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Life Sci. 2022;299:120538. - PubMed
-
- Ghasemi R, Haeri A, Dargahi L, Mohamed Z, Ahmadiani A. Insulin in the Brain:Sources, Localization and Functions. Mol Neurobiol. 2013;47:145–71. - PubMed
-
- Maher MA, Kandeel WA, Hammam OA, Attia YM, Mahmoud S, Salah M. Histopathological Evaluation of Insulin-DMSO Formula Designed for Direct Nose-to-brain Delivery. Histol Histopathol. 2021;37:431–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
