Multimodality matters in numerical communication
- PMID: 37564312
- PMCID: PMC10411739
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1130777
Multimodality matters in numerical communication
Abstract
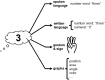
Modern society depends on numerical information, which must be communicated accurately and effectively. Numerical communication is accomplished in different modalities-speech, writing, sign, gesture, graphs, and in naturally occurring settings it almost always involves more than one modality at once. Yet the modalities of numerical communication are often studied in isolation. Here we argue that, to understand and improve numerical communication, we must take seriously this multimodality. We first discuss each modality on its own terms, identifying their commonalities and differences. We then argue that numerical communication is shaped critically by interactions among modalities. We boil down these interactions to four types: one modality can amplify the message of another; it can direct attention to content from another modality (e.g., using a gesture to guide attention to a relevant aspect of a graph); it can explain another modality (e.g., verbally explaining the meaning of an axis in a graph); and it can reinterpret a modality (e.g., framing an upwards-oriented trend as a bad outcome). We conclude by discussing how a focus on multimodality raises entirely new research questions about numerical communication.
Keywords: data visualization; gesture; graphs; multimodality; numerical cognition; numerical communication; quantifiers.
Copyright © 2023 Winter and Marghetis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Remarks on Multimodality: Grammatical Interactions in the Parallel Architecture.Front Artif Intell. 2022 Jan 4;4:778060. doi: 10.3389/frai.2021.778060. eCollection 2021. Front Artif Intell. 2022. PMID: 35059636 Free PMC article.
-
Releasing the constraints on aphasia therapy: the positive impact of gesture and multimodality treatments.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013 May;22(2):S227-39. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2012/12-0091). Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23695899
-
A multimodal parallel architecture: A cognitive framework for multimodal interactions.Cognition. 2016 Jan;146:304-23. doi: 10.1016/j.cognition.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Nov 9. Cognition. 2016. PMID: 26491835 Review.
-
The development of gesture and speech as an integrated system.New Dir Child Dev. 1998 Spring;(79):29-42. doi: 10.1002/cd.23219987903. New Dir Child Dev. 1998. PMID: 9507702
-
The Role of Gesture in Communication and Cognition: Implications for Understanding and Treating Neurogenic Communication Disorders.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Aug 11;14:323. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00323. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32903691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Numbers in Context: Cardinals, Ordinals, and Nominals in American English.Cogn Sci. 2024 Jun;48(6):e13471. doi: 10.1111/cogs.13471. Cogn Sci. 2024. PMID: 38895756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alibali M. W., DiRusso A. A. (1999). The function of gesture in learning to count: more than keeping track. Cogn. Dev. 14, 37–56. doi: 10.1016/S0885-2014(99)80017-3 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

