Pharmacotherapy and pulmonary fibrosis risk after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective nationwide cohort study in the United States
- PMID: 37564420
- PMCID: PMC10410516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lana.2023.100566
Pharmacotherapy and pulmonary fibrosis risk after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective nationwide cohort study in the United States
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by lung parenchymal destruction and can increase morbidity and mortality. Pulmonary fibrosis commonly occurs following hospitalization for SARS-CoV-2 infection. As there are medications that modify pulmonary fibrosis risk, we investigated whether distinct pharmacotherapies (amiodarone, cancer chemotherapy, corticosteroids, and rituximab) are associated with differences in post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis incidence.
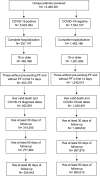
Methods: We used the National COVID-19 Cohort Collaboration (N3C) Data Enclave, which aggregates and harmonizes COVID-19 data across the United States, to assess pulmonary fibrosis incidence documented at least 60 days after COVID-19 diagnosis among adults hospitalized between January 1st, 2020 and July 6th, 2022 without pre-existing pulmonary fibrosis. We used propensity scores to match pre-COVID-19 drug-exposed and unexposed cohorts (1:1) based on covariates with known influence on pulmonary fibrosis incidence, and estimated the association of drug exposure with risk for post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. Sensitivity analyses considered pulmonary fibrosis incidence documented at least 30- or 90-days post-hospitalization and pulmonary fibrosis incidence in the COVID-19-negative N3C population.
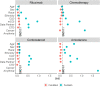
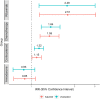
Findings: Among 5,923,394 patients with COVID-19, we analyzed 452,951 hospitalized adults, among whom pulmonary fibrosis incidence was 1.1 per 100-person-years. 277,984 hospitalized adults with COVID-19 were included in our primary analysis, among whom all drug exposed cohorts were well-matched to unexposed cohorts (standardized mean differences <0.1). The post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis incidence rate ratio (IRR) was 2.5 (95% CI 1.2-5.1, P = 0.01) for rituximab, 1.6 (95% CI 1.3-2.0, P < 0.0001) for chemotherapy, and 1.2 (95% CI 1.0-1.3, P = 0.02) for corticosteroids. Amiodarone exposure had no significant association with post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis (IRR = 0.8, 95% CI 0.6-1.1, P = 0.24). In sensitivity analyses, pre-COVID-19 corticosteroid use was not consistently associated with post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. In the COVID-19 negative hospitalized population (n = 1,240,461), pulmonary fibrosis incidence was lower overall (0.6 per 100-person-years) and for patients exposed to all four drugs.
Interpretation: Recent rituximab or cancer chemotherapy before COVID-19 infection in hospitalized patients is associated with increased risk for post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis.
Funding: The analyses described in this publication were conducted with data or tools accessed through the NCATS N3C Data Enclave https://covid.cd2h.org and N3C Attribution & Publication Policy v1.2-2020-08-25b supported by NIHK23HL146942, NIHK08HL150291, NIHK23HL148387, NIHUL1TR002389, NCATSU24 TR002306, and a SECURED grant from the Walder Foundation/Center for Healthcare Delivery Science and Innovation, University of Chicago. WFP received a grant from the Greenwall Foundation. This research was possible because of the patients whose information is included within the data and the organizations (https://ncats.nih.gov/n3c/resources/data-contribution/data-transfer-agreement-signatories) and scientists who have contributed to the on-going development of this community resource (https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocaa196).
Keywords: Pharmacotherapy; Post-COVID; Pulmonary fibrosis; Rituximab; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RB, TJB, VZ, HZ, AES, and RK have nothing to disclose. AA has received speaking and advisory board fees from Genentech and Boehringer Ingelheim and is supported by a career development award from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI K23HL146942), and grant funding from the American College of Chest Physicians and the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. BKP is supported by a career development award from the NHLBI (K23-HL148387) and funding from the Walder Foundation and the Center for Healthcare Delivery Science and Innovation at the University of Chicago. JS has research and training funding from NIH, NSF, and the Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and has a potential financial interest in PulmOne Advanced Medical Diagnostics, Ltd, Israel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association Between Immune Dysfunction and COVID-19 Breakthrough Infection After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in the US.JAMA Intern Med. 2022 Feb 1;182(2):153-162. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.7024. JAMA Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34962505 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of post-acute COVID-19 symptoms across healthcare settings in seven countries: an international retrospective cohort study using routinely-collected data.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Oct 30;77:102903. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102903. eCollection 2024 Nov. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39552716 Free PMC article.
-
Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections and prediction of moderate-to-severe outcomes during rituximab therapy in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in the UK: a single-centre cohort study.Lancet Rheumatol. 2023 Feb;5(2):e88-e98. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00004-8. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36712951 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and mortality due to thromboembolic events during the COVID-19 pandemic: Multi-sourced population-based health records cohort study.Thromb Res. 2021 Jun;202:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Thromb Res. 2021. PMID: 33711754 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of recovery rate and predictors among hospitalized COVID- 19 infected patients in Ethiopia; a systemic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 3;25(1):1644. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22841-x. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40319254 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Computer-Aided Pulmonary Fibrosis Detection Leveraging an Advanced Artificial Intelligence Triage and Notification Software.J Clin Med Res. 2023 Sep;15(8-9):423-429. doi: 10.14740/jocmr5020. Epub 2023 Sep 30. J Clin Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37822853 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Acute Phase: Long-Term Impact of COVID-19 on Functional Capacity and Prothrombotic Risk-A Pilot Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 27;60(1):51. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010051. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38256314 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis: National Database Analysis.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 21;12(12):2650. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122650. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767557 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic lung inflammation and CK14+ basal cell proliferation induce persistent alveolar-bronchiolization in SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105363. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105363. Epub 2024 Sep 25. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39326207 Free PMC article.
-
Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 30;17(6):709. doi: 10.3390/ph17060709. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR002649/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL146942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001860/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104942/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL148387/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004404/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001445/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003096/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 TR004556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104938/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002537/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001412/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002736/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002369/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002541/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115371/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002538/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115458/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002535/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001409/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001453/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003107/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003015/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002733/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 TR002306/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001876/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001436/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002384/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002553/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002389/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104941/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002014/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002550/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002556/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003017/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002645/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002366/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115428/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002377/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115677/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002544/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003098/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

