Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators Topography for "Island Transverse Rectus Abdominis Musculocutaneous Flap" in Breast Reconstruction
- PMID: 37564712
- PMCID: PMC10411245
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2093-8323
Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators Topography for "Island Transverse Rectus Abdominis Musculocutaneous Flap" in Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
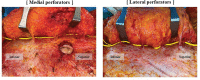
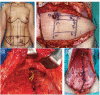
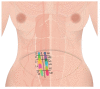
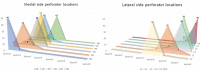
Background The Island transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) flap is well vascularized with very reliable blood flow, because all perforators of the zone I are included when it is harvested. The number of perforators, topographic mapping, and their relationship with reconstructed outcomes were investigated. Methods Fifty patients with Island TRAM breast reconstruction from September 2021 to August 2022 were investigated. The zone I was divided into a total of eight sections. Under the loupe magnification, all perforators larger than 0.5 mm in zone I were counted with fine dissection, and photographs were taken in background of vessel loops. Complications like flap necrosis, seroma, and hematoma were also investigated. Result There are 12 ideal perforators on average in zone I such as one perforator in section I, II, IV, V, VI, VIII, and three perforators in section III and VII. However, two perforators (M6 and L6) below arcuate line were sacrificed in the time of flap harvest to prevent hernia. Island TRAM included 10 perforators on average (5 perforators in each side) above arcuate line to be transferred to the recipient site. Only minor complications were identified. Conclusion The Island TRAM flap includes 10 perforators to get the vigorous blood flow. The periumbilical to upper medial perforators become more dominant in the perfusion of the flap after deep inferior epigastric artery division. Well preserved perforators will guarantee the satisfactory breast reconstruction with the least complication.
Keywords: Island TRAM flap; breast reconstruction; perforators; topographic mapping.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perforator topography of the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap in 100 cases of breast reconstruction.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002 May;109(6):1912-8. doi: 10.1097/00006534-200205000-00021. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. PMID: 11994593
-
Rezoning Free Muscle-Sparing Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flaps Based on Perforasome Groupings and a New Understanding of the Vascular Architecture of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery-Based Flaps.Ann Plast Surg. 2019 Dec;83(6):e59-e67. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001859. Ann Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31232810
-
Perforator number predicts fat necrosis in a prospective analysis of breast reconstruction with free TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA flaps.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010 May;125(5):1335-1341. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181d4fb4a. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20440154
-
Is Unipedicled Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap Obsolete Owing to Superiority of DIEP Flap?Ann Plast Surg. 2018 Jun;80(6S Suppl 6):S418-S420. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000001319. Ann Plast Surg. 2018. PMID: 29369109 Review.
-
Preoperative cross-sectional mapping for deep inferior epigastric and profunda artery perforator flaps.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019 Aug;9(Suppl 1):S131-S142. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2018.10.03. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 31559159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buck D W, II, Fine N A. The pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap: indications, techniques, and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;124(04):1047–1054. - PubMed
-
- Hartrampf C R., Jr The transverse abdominal island flap for breast reconstruction. A 7-year experience. Clin Plast Surg. 1988;15(04):703–716. - PubMed
-
- Yoon J S, Oh J, Chung M S, Ahn H C. The island-type pedicled TRAM flap: Improvement of the aesthetic outcomes of breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020;73(06):1060–1067. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj A K, Chevray P M, Chang D W.Comparison of donor-site complications and functional outcomes in free muscle-sparing TRAM flap and free DIEP flap breast reconstruction Plast Reconstr Surg 200611703737–746., discussion 747–750 - PubMed
-
- Garvey P B, Buchel E W, Pockaj B Aet al.DIEP and pedicled TRAM flaps: a comparison of outcomes Plast Reconstr Surg 2006117061711–1719., discussion 1720–1721 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

