Ufmylation of UFBP1 Is Dispensable for Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response, Embryonic Development, and Cardiac and Intestinal Homeostasis
- PMID: 37566002
- PMCID: PMC10416869
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12151923
Ufmylation of UFBP1 Is Dispensable for Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response, Embryonic Development, and Cardiac and Intestinal Homeostasis
Abstract
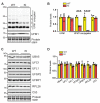
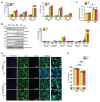
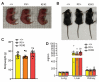
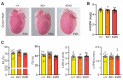
Protein modification by ubiquitin fold modifier 1 (UFM1), termed ufmylation, regulates various physiological and pathological processes. Among emerging UFM1 targets, UFM1 binding protein 1 (UFBP1) is the first identified ufmylation substrate. Recent clinical and animal studies have demonstrated the pivotal roles of UFBP1 in development, hematopoiesis, intestinal homeostasis, chondrogenesis, and neuronal development, which has been linked to its function in maintaining endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis. However, the importance of UFBP1 ufmylation in these cellular and physiological processes has yet to be determined. It has been proposed that ufmylation of lysine 268 (267 in humans) in UFBP1 plays a critical role in mediating the effects of the ufmylation pathway. In this study, we for the first time probe the pathophysiological significance of UFBP1 ufmylation in vivo by creating and characterizing a mouse UFBP1 knockin (KI) model in which the lysine 268 of UFBP1, the amino acid accepting UFM1, was mutated to arginine. Our results showed that the K268R mutation reduced the total ufmylated proteins without altering the expression levels of individual ufmylation enzymes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The K268R mutation did not alter ER stress-stimuli-induced ER stress signaling or cell death in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The homozygous KI mice were viable and morphologically indistinguishable from their littermate wild-type controls up to one year of age. Serial echocardiography revealed no cardiac functional impairment of the homozygous KI mice. Furthermore, the homozygous KI mice exhibited the same susceptibility to dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) -induced colitis as wild-type mice. Taken together, these results suggest that UFBP1 K268 is dispensable for ER stress response, embryonic development, cardiac homeostasis under physiological conditions, and intestinal homeostasis under pathological conditions. Our studies call for future investigations to understand the biological function of UFBP1 ufmylation and offer a new mouse model to determine the roles of UFBP1 ufmylation in different tissues under stress conditions.
Keywords: ER stress response; UFBP1; UFM1; heart failure; intestine; ufmylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
UFBP1, a Key Component of the Ufm1 Conjugation System, Is Essential for Ufmylation-Mediated Regulation of Erythroid Development.PLoS Genet. 2015 Nov 6;11(11):e1005643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005643. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26544067 Free PMC article.
-
Ufmylation on UFBP1 alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 2;14(9):584. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06095-2. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37660122 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the roles of the UFM1 E3 ligase complex in ufmylation and ribosome-associated protein quality control.Sci Adv. 2023 Aug 18;9(33):eadh3635. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh3635. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37595036 Free PMC article.
-
A guide to UFMylation, an emerging posttranslational modification.FEBS J. 2023 Nov;290(21):5040-5056. doi: 10.1111/febs.16730. Epub 2023 Feb 8. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 36680403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted roles of UFMylation in health and disease.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Apr;46(4):805-815. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01456-9. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39775503 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of neurofibromin induces inflammatory macrophage phenotypic switch and retinal neovascularization via GLUT1 activation.Cell Rep. 2025 May 27;44(5):115625. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115625. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40279245 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the functional role of UFMylation in cells (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):191. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13556. Epub 2025 May 9. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40341950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muona M., Ishimura R., Laari A., Ichimura Y., Linnankivi T., Keski-Filppula R., Herva R., Rantala H., Paetau A., Poyhonen M., et al. Biallelic Variants in UBA5 Link Dysfunctional UFM1 Ubiquitin-like Modifier Pathway to Severe Infantile–Onset Encephalopathy. Am J. Hum Genet. 2016;99:683–694. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.06.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

