Hybrid Closed-Loop Therapy in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes and Above-Target HbA1c: A Real-world Observational Study
- PMID: 37566697
- PMCID: PMC10516256
- DOI: 10.2337/dc23-0635
Hybrid Closed-Loop Therapy in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes and Above-Target HbA1c: A Real-world Observational Study
Abstract
Objective: We explored longitudinal changes associated with switching to hybrid closed-loop (HCL) insulin delivery systems in adults with type 1 diabetes and elevated HbA1c levels despite the use of intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring (isCGM) and insulin pump therapy.
Research design and methods: We undertook a pragmatic, preplanned observational study of participants included in the National Health Service England closed-loop pilot. Adults using isCGM and insulin pump across 31 diabetes centers in England with an HbA1c ≥8.5% who were willing to commence HCL therapy were included. Outcomes included change in HbA1c, sensor glucometrics, diabetes distress score, Gold score (hypoglycemia awareness), acute event rates, and user opinion of HCL.
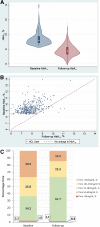
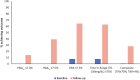
Results: In total, 570 HCL users were included (median age 40 [IQR 29-50] years, 67% female, and 85% White). Mean baseline HbA1c was 9.4 ± 0.9% (78.9 ± 9.1 mmol/mol) with a median follow-up of 5.1 (IQR 3.9-6.6) months. Of 520 users continuing HCL at follow-up, mean adjusted HbA1c reduced by 1.7% (95% CI 1.5, 1.8; P < 0.0001) (18.1 mmol/mol [95% CI 16.6, 19.6]; P < 0.0001). Time in range (70-180 mg/dL) increased from 34.2 to 61.9% (P < 0.001). Individuals with HbA1c of ≤58 mmol/mol rose from 0 to 39.4% (P < 0.0001), and those achieving ≥70% glucose time in range and <4% time below range increased from 0.8 to 28.2% (P < 0.0001). Almost all participants rated HCL therapy as having a positive impact on quality of life (94.7% [540 of 570]).
Conclusions: Use of HCL is associated with improvements in HbA1c, time in range, hypoglycemia, and diabetes-related distress and quality of life in people with type 1 diabetes in the real world.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- NHS Digital . National Diabetes Audit Core report 1: care processes and treatment targets 2021-22, underlying data, 2023. Accessed 5 February 2023. Available from https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/nat...
-
- Gregory GA, Robinson TIG, Linklater SE, et al.; International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group . Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:741–760 - PubMed
-
- NHS Digital . National Diabetes Insulin Pump Audit, 2017-18, 2018. Accessed 6 February 2023. Available from https://files.digital.nhs.uk/E0/030704/National%20Diabetes%20Insulin%20P...
-
- Chatwin H, Broadley M, Speight J, et al.; Hypo-RESOLVE Consortium . The impact of hypoglycaemia on quality of life outcomes among adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2021;174:108752. - PubMed
-
- Griffin TP, Gallen G, Hartnell S, et al. UK’s Association of British Clinical Diabetologist’s Diabetes Technology Network (ABCD-DTN): best practice guide for hybrid closed-loop therapy. Diabet Med 2023;40:e15078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

