Is Exercise during Pregnancy a Risk for Gestational Age and Preterm Delivery? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37568315
- PMCID: PMC10419377
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12154915
Is Exercise during Pregnancy a Risk for Gestational Age and Preterm Delivery? Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
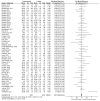
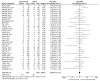
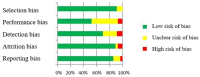
Traditionally, one of the primary concerns regarding exercise during pregnancy has been the potential of reducing gestational age and increasing the likelihood of preterm delivery. The aim of this study was to perform a systematic review about the effects of physical activity (PA) during pregnancy on gestational age and preterm delivery. A systematic review and two meta-analyses were performed (Registration No. CRD42022370770). Data sources from online databases were searched up to November 2022. The review exclusively included studies involving pregnant populations and interventions consisting of PA implemented during pregnancy. The primary outcomes analysed were gestational age, measured in weeks, and the occurrence of preterm deliveries. A total of 57 studies were analysed through two independent meta-analyses for the first one, no association was found between moderate exercise during pregnancy and gestational age (Z = 0.45, p = 0.65, ES = 0.08, 95% CI = -0.06-0.04, I2 = 42%, P heterogeneity = 0.001), showing the exercise group had a higher gestational age. In addition, no differences were found between groups in terms of number of preterm deliveries (RR = 0.96, (95% CI = 0.77-1.21, Z = 0.33, p = 0.74; ES = 0.07; I2 = 31%, P heterogeneity = 0.05)). The findings of this study indicate that there is no association between exercise during pregnancy and reduced gestational age or increased risk of preterm delivery in healthy pregnancies.
Keywords: exercise; gestational age; pregnancy; preterm delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
Effect of levothyroxine supplementation on pregnancy loss and preterm birth in women with subclinical hypothyroidism and thyroid autoimmunity: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 May 1;25(3):344-361. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz003. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30951172
-
Effects of physical exercise during pregnancy on maternal and infant outcomes in overweight and obese pregnant women: A meta-analysis.Birth. 2019 Jun;46(2):211-221. doi: 10.1111/birt.12396. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Birth. 2019. PMID: 30240042
-
Risk of stillbirth, preterm delivery, and fetal growth restriction following exposure in a previous birth: systematic review and meta-analysis.BJOG. 2018 Jan;125(2):183-192. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14906. Epub 2017 Oct 3. BJOG. 2018. PMID: 28856792
-
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Long-term Maternal Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Feb 5;3(2):e1920964. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20964. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32049292
Cited by
-
Characteristics, Physiopathology and Management of Dyslipidemias in Pregnancy: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 1;16(17):2927. doi: 10.3390/nu16172927. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barakat R. Pregnancy. In: Mooren F.-C., editor. Encyclopedia of Exercise Medicine in Health and Disease. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. pp. 722–726.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

