Correlation between Inflammatory Systemic Biomarkers and Surgical Trauma in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
- PMID: 37568549
- PMCID: PMC10419519
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12155147
Correlation between Inflammatory Systemic Biomarkers and Surgical Trauma in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures
Abstract
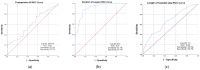
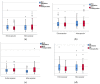
The treatment for hip fractures consists of a wide variety of orthopedic implants ranging from prosthesis to intramedullary nails. The purpose of this study is to determine the correlation between blood-count-derived biomarkers such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), the monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) and the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and the level of aggression sustained by elderly patients during these surgical procedures. A total of 129 patients aged over 70 and diagnosed with acute hip fractures who underwent surgical treatment between November 2021 and February 2023 were included in our observational retrospective cohort study. Two groups were formed depending on the anatomic location of the fracture for statistical comparison: group 1 with extracapsular fractures, who received a closed reduction internal fixation (CRIF) with a gamma nail (GN) as treatment, and group 2 with intracapsular fractures, who received a bipolar hemiarthroplasty (BHA) as treatment. The length of hospital stay (LHS), duration of surgery, preoperative days, pre- and postoperative red blood count (RBC) and hemoglobin (HGB) levels and postoperative NLR, PLR and SII were significantly different between the two groups (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the multivariate analysis indicated that the postoperative NLR (p = 0.029), PLR (p = 0.009), SII (p = 0.001) and duration of surgery (p < 0.0001) were independently related to the invasiveness of the procedures. The ROC curve analysis demonstrated that a postoperative SII > 1564.74 is a more reliable predictor of surgical trauma in terms of specificity (58.1%) and sensitivity (56.7%). Postoperative SII as a biomarker appears to be closely correlated with surgical trauma sustained by an older population with hip fractures.
Keywords: bipolar hemiarthroplasty; extracapsular; gamma nail; hip fractures; intracapsular; monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schemitsch E.H., Miclau T., Karachalios T., Nowak L.L., Sancheti P., Poolman R.W., Caminis J., Daizadeh N., Dent-Acosta R.E., Egbuna O., et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Romosozumab for the Treatment of Hip Fractures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2020;102:693–702. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.19.00790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

