Portrait of the Inflammatory Response to Radioiodine Therapy in Female Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with/without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 37568611
- PMCID: PMC10417100
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15153793
Portrait of the Inflammatory Response to Radioiodine Therapy in Female Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with/without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
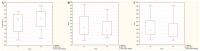
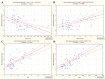
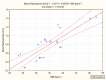
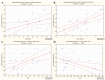
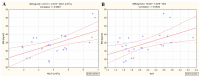
No clinical studies have investigated the effect of radioiodine (131I)-targeted therapy on the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as inflammatory response markers in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity. This study aimed to assess the relationship between blood radioactivity, body mass index (BMI), and peripheral blood cells three days after 131I intake in 56 female patients without T2DM (DTC/-T2DM) vs. 24 female patients with T2DM (DTC/+T2DM). Blood radioactivity, measured three days after 131I intake, was significantly lower in the DTC/+T2DM than in the DTC/-T2DM patients (0.7 mCi vs. 1.5 mCi, p < 0.001). The relationship between blood radioactivity and BMI (r = 0.83, p < 0.001), blood radioactivity and NLR (r = 0.53, p = 0.008), and BMI and NLR (r = 0.58, p = 0.003) indicates a possible connection between the bloodstream 131I uptake and T2DM-specific chronic inflammation. In patients without T2DM, 131I therapy has immunosuppressive effects, leading to increased NLR (19.6%, p = 0.009) and PLR (39.1%, p = 0.002). On the contrary, in the chronic inflammation context of T2DM, 131I therapy amplifies immune metabolism, leading to a drop in NLR (10%, p = 0.032) and PLR (13.4%, p = 0.021). Our results show that, in DTC/+T2DM, the bidirectional crosstalk between neutrophils and obesity may limit 131I uptake in the bloodstream. Considering the immune response to 131I therapy, the two groups of patients can be seen as a synchronous portrait of two sides. The explanation could lie in the different radiosensitivity of T and B lymphocytes, with T lymphocytes being predominant in patients with DTC/-T2DM and, most likely, B lymphocytes being predominant in T2DM.
Keywords: 131I; BMI; NLR; PLR; blood radioactivity; differentiated thyroid cancer; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Atlas. 10th ed. [(accessed on 14 February 2023)]. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/
-
- Tuttle R.M., Ahuja S., Avram A.M., Bernet V.J., Bourguet P., Daniels G.H., Dillehay G., Draganescu C., Flux G., Führer D., et al. Controversies, Consensus, and Collaboration in the Use of 131I Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Joint Statement from the American Thyroid Association, the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the European Thyroid Association. Thyroid. 2019;29:461–470. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0597. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

