Polyphenol-Based Nanoparticles: A Promising Frontier for Enhanced Colorectal Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 37568642
- PMCID: PMC10416951
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15153826
Polyphenol-Based Nanoparticles: A Promising Frontier for Enhanced Colorectal Cancer Treatment
Abstract
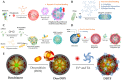
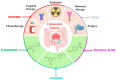
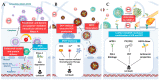
Colorectal cancer (CRC) poses a significant challenge in healthcare, necessitating the exploration of novel therapeutic strategies. Natural compounds such as polyphenols with inherent anticancer properties have gained attention as potential therapeutic agents. This review highlights the need for novel therapeutic approaches in CRC, followed by a discussion on the synthesis of polyphenols-based nanoparticles. Various synthesis techniques, including dynamic covalent bonding, non-covalent bonding, polymerization, chemical conjugation, reduction, and metal-polyphenol networks, are explored. The mechanisms of action of these nanoparticles, encompassing passive and active targeting mechanisms, are also discussed. The review further examines the intrinsic anticancer activity of polyphenols and their enhancement through nano-based delivery systems. This section explores the natural anticancer properties of polyphenols and investigates different nano-based delivery systems, such as micelles, nanogels, liposomes, nanoemulsions, gold nanoparticles, mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and metal-organic frameworks. The review concludes by emphasizing the potential of nanoparticle-based strategies utilizing polyphenols for CRC treatment and highlights the need for future research to optimize their efficacy and safety. Overall, this review provides valuable insights into the synthesis, mechanisms of action, intrinsic anticancer activity, and enhancement of polyphenols-based nanoparticles for CRC treatment.
Keywords: cancer cell death; chemical synthesis; colorectal cancer; drug delivery system; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; natural compounds; polyphenols; signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aquina C.T., Mohile S.G., Tejani M.A., Becerra A.Z., Xu Z., Hensley B.J., Arsalani-Zadeh R., Boscoe F.P., Schymura M.J., Noyes K., et al. The impact of age on complications, survival, and cause of death following colon cancer surgery. Br. J. Cancer. 2017;116:389–397. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.421. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shiri P., Ramezanpour S., Amani A.M., Dehaen W. A patent review on efficient strategies for the total synthesis of pazopanib, regorafenib and lenvatinib as novel anti-angiogenesis receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Mol. Divers. 2022;26:2981–3002. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10406-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

