Deep Learning in Diagnosis of Dental Anomalies and Diseases: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37568875
- PMCID: PMC10416832
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13152512
Deep Learning in Diagnosis of Dental Anomalies and Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Deep learning and diagnostic applications in oral and dental health have received significant attention recently. In this review, studies applying deep learning to diagnose anomalies and diseases in dental image material were systematically compiled, and their datasets, methodologies, test processes, explainable artificial intelligence methods, and findings were analyzed. Tests and results in studies involving human-artificial intelligence comparisons are discussed in detail to draw attention to the clinical importance of deep learning. In addition, the review critically evaluates the literature to guide and further develop future studies in this field. An extensive literature search was conducted for the 2019-May 2023 range using the Medline (PubMed) and Google Scholar databases to identify eligible articles, and 101 studies were shortlisted, including applications for diagnosing dental anomalies (n = 22) and diseases (n = 79) using deep learning for classification, object detection, and segmentation tasks. According to the results, the most commonly used task type was classification (n = 51), the most commonly used dental image material was panoramic radiographs (n = 55), and the most frequently used performance metric was sensitivity/recall/true positive rate (n = 87) and accuracy (n = 69). Dataset sizes ranged from 60 to 12,179 images. Although deep learning algorithms are used as individual or at least individualized architectures, standardized architectures such as pre-trained CNNs, Faster R-CNN, YOLO, and U-Net have been used in most studies. Few studies have used the explainable AI method (n = 22) and applied tests comparing human and artificial intelligence (n = 21). Deep learning is promising for better diagnosis and treatment planning in dentistry based on the high-performance results reported by the studies. For all that, their safety should be demonstrated using a more reproducible and comparable methodology, including tests with information about their clinical applicability, by defining a standard set of tests and performance metrics.
Keywords: convolutional neural network; deep learning; dental anomalies and diseases; dental diagnostics; dental images.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
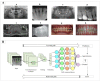
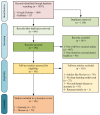
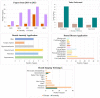
References
-
- WHO . Global Oral Health Status Report: Towards Universal Health Coverage for Oral Health by 2030. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022.
-
- Folly P. Imaging Techniques in Dental Radiology: Acquisition, Anatomic Analysis and Interpretation of Radiographic Images. BDJ Stud. 2021;28:11. doi: 10.1038/s41406-021-0258-7. - DOI
-
- Haq I., Mazhar T., Malik M.A., Kamal M.M., Ullah I., Kim T., Hamdi M., Hamam H. Lung Nodules Localization and Report Analysis from Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan Using a Novel Machine Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:12614. doi: 10.3390/app122412614. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

