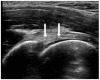
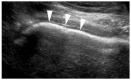
The Role of Ultrasonography in Hip Impingement Syndromes: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37568972
- PMCID: PMC10416868
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13152609
The Role of Ultrasonography in Hip Impingement Syndromes: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Hip pain is indubitably a frequent clinical problem deriving from copious etiologies. Hip impingement syndromes are one of the most prevalent causes of persistent groin pain, especially in young and active patients. Diligent imaging of the hip region is indispensable to discern femoroacetabular impingement, as the differential diagnosis of hip pain can be exceedingly arduous. Despite hip radiography being plain and broadly attainable, it offers narrow information concerning soft tissue pathologies around the hip joint (extra-articular hip impingement syndromes). Magnetic resonance imaging and arthrography remain the gold standard examination for detecting intra-articular pathologies; however, they are widely considered expensive, time-consuming and characterized by confined. Consequently, ultrasonography has emerged as an alternative valuable diagnostic tool for distinguishing the underlying abnormalities that trigger femoroacetabular impingement. Proper hip ultrasound examination provides dynamic assessment, while also beneficial for guided intervention around the hip joint. Ultrasound hip examination is exacting due to its complex regional anatomy and deep location. It is capable of providing detailed information about various hip quadrants. An adept operator can identify both intra-articular and extra-articular pathologies. In addition, with ultrasonography, hip injections have been rendered relatively undemanding, aiding in therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. This paper aims to provide a succinct and compendious review of the existing literature, accentuating the crucial role of ultrasonography in diagnosing hip impingement syndromes and determining whether an additional examination is required regarding distinguishing between intra-articular and extra-articular syndromes.
Keywords: acetabulum; femoral head; femoroacetabular impingement; groin pain; hip; hip pain; review; ultrasonography; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chamberlain R. Hip Pain in Adults: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. Am. Fam. Physician. 2021;103:81–89. - PubMed
-
- Wilson J.J., Furukawa M. Evaluation of the patient with hip pain. Am. Fam. Physician. 2014;89:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Nepple J.J., Prather H., Trousdale R.T., Clohisy J.C., Beaulé P.E., Glyn-Jones S., Kim Y.-J. Clinical diagnosis of femoroacetabular impingement. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2013;21:S16–S19. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources