Advances in Microfluidics Techniques for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues in Food
- PMID: 37569137
- PMCID: PMC10417549
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12152868
Advances in Microfluidics Techniques for Rapid Detection of Pesticide Residues in Food
Abstract
Food safety is a significant issue that affects people worldwide and is tied to their lives and health. The issue of pesticide residues in food is just one of many issues related to food safety, which leave residues in crops and are transferred through the food chain to human consumption. Foods contaminated with pesticide residues pose a serious risk to human health, including carcinogenicity, neurotoxicity, and endocrine disruption. Although traditional methods, including gas chromatography, high-performance liquid chromatography, chromatography, and mass spectrometry, can be used to achieve a quantitative analysis of pesticide residues, the disadvantages of these techniques, such as being time-consuming and costly and requiring specialist staff, limit their application. Therefore, there is a need to develop rapid, effective, and sensitive equipment for the quantitative analysis of pesticide residues in food. Microfluidics is rapidly emerging in a number of fields due to its outstanding strengths. This paper summarizes the application of microfluidic techniques to pyrethroid, carbamate, organochlorine, and organophosphate pesticides, as well as to commercial products. Meanwhile, the study also outlines the development of microfluidics in combination with 3D printing technology and nanomaterials for detecting pesticide residues in food.
Keywords: food samples; microfluidic; pesticide residues; rapid detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



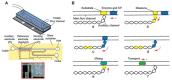



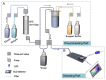

References
-
- Weng X., Neethirajan S. Ensuring food safety: Quality monitoring using microfluidics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017;65:10–22. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.04.015. - DOI
-
- Lin X.D., Ibarlucea B., Peng T., Shen R., Li P.Y., Zhang P. Two birds with one stone: A multifunctional nanoplatform for photothermal sensitive detection and real-time inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus with NIR responsive Cu2_XSe@Van NPs. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2023;381:133475. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2023.133475. - DOI
-
- Shrestha S., Parks C.G., Goldner W.S., Kamel F., Umbach D.M., Ward M.H., Lerro C.C., Koutros S., Hofmann J.N., Freeman L.E.B., et al. Pesticide Use and Incident Hypothyroidism in Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018;126:097008. doi: 10.1289/EHP3194. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 52075138/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22KJB150050/Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China
- CX(21)3162/Jiangsu Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Fund
- KJ2023076/Market Supervision Administration Science and Technology Fund of Jiangsu Province
- KYCX22_3479/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

