Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37569265
- PMCID: PMC10419199
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241511888
Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to evaluate the current evidence in relation to the clinicopathological and prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) overexpression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). We searched MEDLINE/PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Scopus for studies published before November 2022. We evaluated the quality of primary-level studies using the QUIPS tool, conducted meta-analyses, examined inter-study heterogeneity via subgroup analyses and meta-regressions, and performed small-study effects analyses. Fifty primary-level studies (4631 patients) met the inclusion criteria. EGFR overexpression was significantly associated with poor overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.38, 95% confidence intervals [CI] = 1.06-1.79, p = 0.02), N+ status (odds ratio [OR] = 1.37, 95%CI = 1.01-1.86, p = 0.04), and moderately-poorly differentiated OSCC (OR = 1.43, 95% CI = 1.05-1.94, p = 0.02). In addition, better results were obtained by the application of a cutoff point ≥10% tumor cells with EGFR overexpression (p < 0.001). In conclusion, our systematic review and meta-analysis supports that the immunohistochemical assessment of EGFR overexpression may be useful as a prognostic biomarker for OSCC.
Keywords: EGFR; epidermal growth factor receptor; meta-analysis; oral cancer; prognosis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

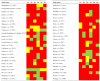
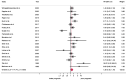
Similar articles
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of cyclin D1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Oral Oncol. 2018 Aug;83:96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Oral Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30098785
-
Prognostic value of EGFR and p-EGFR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jan 21;101(3):e28507. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028507. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35060503 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of survivin expression in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: evidence from a meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 24;10(2):e0116517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116517. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25710884 Free PMC article.
-
c-Met expression is a marker of poor prognosis in patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Mar 1;88(3):701-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.11.013. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24521684
-
Prognostic role of epidermal growth factor receptor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Head Neck. 2014 Oct;36(10):1508-16. doi: 10.1002/hed.23481. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Head Neck. 2014. PMID: 23996630 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Asperosaponin VI Related to EGFR/MMP9/AKT/PI3K Pathway in Treatment of Rheumtoid Arthritis.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Feb;31(2):131-141. doi: 10.1007/s11655-024-3767-8. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 39499411
-
Molecular and Genetic Pathogenesis of Oral Cancer: A Basis for Customized Diagnosis and Treatment.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;14(7):842. doi: 10.3390/biology14070842. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) upregulation in the prediction of the malignant transformation risk in oral potentially malignant disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oral Health. 2025 Mar 27;6:1578561. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1578561. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40213513 Free PMC article.
-
A Molecular Hypothesis on Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cancer Hallmarks Expression in This Oral Potentially Malignant Disorder.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;16(15):2614. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152614. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Molecular Diagnosis and Comprehensive Treatment of Oral Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 12;47(6):452. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060452. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

