Stringent Response Factor DksA Contributes to Fatty Acid Degradation Function to Influence Cell Membrane Stability and Polymyxin B Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica
- PMID: 37569327
- PMCID: PMC10418728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241511951
Stringent Response Factor DksA Contributes to Fatty Acid Degradation Function to Influence Cell Membrane Stability and Polymyxin B Resistance of Yersinia enterocolitica
Abstract
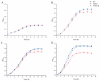
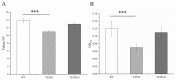
DksA is a proteobacterial regulator that binds directly to the secondary channel of RNA polymerase with (p)ppGpp and is responsible for various bacterial physiological activities. While (p)ppGpp is known to be involved in the regulation and response of fatty acid metabolism pathways in many foodborne pathogens, the role of DksA in this process has yet to be clarified. This study aimed to characterize the function of DksA on fatty acid metabolism and cell membrane structure in Yersinia enterocolitica. Therefore, comparison analysis of gene expression, growth conditions, and membrane permeabilization among the wide-type (WT), DksA-deficient mutant (YEND), and the complemented strain was carried out. It confirmed that deletion of DksA led to a more than four-fold decrease in the expression of fatty acid degradation genes, including fadADEIJ. Additionally, YEND exhibited a smaller growth gap compared to the WT strain at low temperatures, indicating that DksA is not required for the growth of Y. enterocolitica in cold environments. Given that polymyxin B is a cationic antimicrobial peptide that targets the cell membrane, the roles of DksA under polymyxin B exposure were also characterized. It was found that DksA positively regulates the integrity of the inner and outer membranes of Y. enterocolitica under polymyxin B, preventing the leakage of intracellular nucleic acids and proteins and ultimately reducing the sensitivity of Y. enterocolitica to polymyxin B. Taken together, this study provides insights into the functions of DksA and paves the way for novel fungicide development.
Keywords: DksA; Yersinia enterocolitica; fatty acid metabolism; polymyxin B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Key Roles of (p)ppGpp and DksA in Regulating Metabolism and Chemotaxis in Yersinia enterocolitica.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 20;24(8):7612. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087612. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108773 Free PMC article.
-
Similar and Divergent Roles of Stringent Regulator (p)ppGpp and DksA on Pleiotropic Phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0205522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02055-22. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36409141 Free PMC article.
-
(p)ppGpp and DksA play a crucial role in reducing the efficacy of β-lactam antibiotics by modulating bacterial membrane permeability.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr;13(4):e0116924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01169-24. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39992161 Free PMC article.
-
DksA and DNA double-strand break repair.Curr Genet. 2019 Dec;65(6):1297-1300. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00983-x. Epub 2019 May 10. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31076845 Review.
-
Direct binding targets of the stringent response alarmone (p)ppGpp.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Sep;85(6):1029-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08177.x. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22812515 Review.
Cited by
-
In-host evolution of Yersinia enterocolitica during a chronic human infection.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5637. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60782-6. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40595576 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights on challenges encountered with phage therapy against gastrointestinal-associated infections.Gut Pathog. 2025 Aug 11;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13099-025-00735-y. Gut Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40790209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dein W., Bukola A.O. Food safety incidents in the red meat industry: A review of foodborne disease outbreaks linked to the consumption of red meat and its products, 1991 to 2021. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023:110240. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

