The Sigma Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease: New Potential Targets for Diagnosis and Therapy
- PMID: 37569401
- PMCID: PMC10418732
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512025
The Sigma Receptors in Alzheimer's Disease: New Potential Targets for Diagnosis and Therapy
Abstract
Sigma (σ) receptors are a class of unique proteins with two subtypes: the sigma-1 (σ1) receptor which is situated at the mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane (MAM), and the sigma-2 (σ2) receptor, located in the ER-resident membrane. Increasing evidence indicates the involvement of both σ1 and σ2 receptors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), and thus these receptors represent two potentially effective biomarkers for emerging AD therapies. The availability of optimal radioligands for positron emission tomography (PET) neuroimaging of the σ1 and σ2 receptors in humans will provide tools to monitor AD progression and treatment outcomes. In this review, we first summarize the significance of both receptors in the pathophysiology of AD and highlight AD therapeutic strategies related to the σ1 and σ2 receptors. We then survey the potential PET radioligands, with an emphasis on the requirements of optimal radioligands for imaging the σ1 or σ2 receptors in humans. Finally, we discuss current challenges in the development of PET radioligands for the σ1 or σ2 receptors, and the opportunities for neuroimaging to elucidate the σ1 and σ2 receptors as novel biomarkers for early AD diagnosis, and for monitoring of disease progression and AD drug efficacy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; diagnosis; neuroimaging; positron emission tomography; sigma-1 receptor; sigma-2 receptor; therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
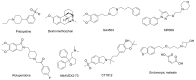
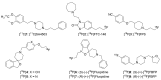
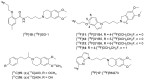
References
-
- Gauthier S., Webster C., Servaes S., Morais J.A., Rosa-Neto P. World Alzheimer Report 2022: Life after Diagnosis: Navigating Treatment, Care and Support. Alzheimer’s Disease International; London, UK: 2022.
-
- Jack C.R., Jr., Bennett D.A., Blennow K., Carrillo M.C., Dunn B., Haeberlein S.B., Holtzman D.M., Jagust W., Jessen F., Karlawish J., et al. NIA-AA research framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:535–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knopman D.S., Haeberlein S.B., Carrillo M.C., Hendrix J.A., Kerchner G., Margolin R., Maruff P., Miller D.S., Tong G., Tome M.B., et al. The national institute on aging and the Alzheimer’s association research framework for Alzheimer’s disease: Perspectives from the research roundtable. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:563–575. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.03.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

