Augmented Placental Protein 13 in Placental-Associated Extracellular Vesicles in Term and Preterm Preeclampsia Is Further Elevated by Corticosteroids
- PMID: 37569423
- PMCID: PMC10419231
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512051
Augmented Placental Protein 13 in Placental-Associated Extracellular Vesicles in Term and Preterm Preeclampsia Is Further Elevated by Corticosteroids
Abstract
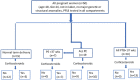
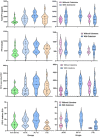
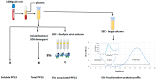
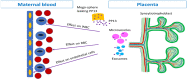
Placental protein 13 (PP13) is a regulatory protein involved in remodeling the vascular system of the pregnancy and extending the immune tolerance of the mother to the growing fetus. PP13 is localized on the surface of the syncytiotrophoblast. An ex vivo placental model shows that the PP13 is released via placental-associated extracellular vesicles (PEVs) to the maternal uterine vein. This exploratory study aimed to determine PEV-associated PP13 in the maternal circulation as compared to the known soluble fraction since each has a specific communication pathway. Patients admitted to Bnai Zion Medical Center for delivery were recruited, and included 19 preeclampsia (PE) patients (7 preterm PE gestational age < 37 weeks' gestation), 16 preterm delivery (PTD, delivery at GA < 37 weeks' gestation), and 15 matched term delivery controls. Treatment by corticosteroids (Celestone), which is often given to patients with suspected preterm PE and PTD, was recorded. The PEV proteome was purified from the patients' plasma by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to separate the soluble and PEV-associated PP13. The total level of PP13 (soluble and PEV-associated) was determined using mild detergent that depleted the PEV proteome. PP13 fractions were determined by ELISA with PP13 specific antibodies. ELISA with alkaline phosphatase (PLAP)- and cluster differentiation 63 (CD63)-specific antibodies served to verify the placental origin of the PEVs. SPSS was used for statistical analysis. The patients' medical, pregnancy, and delivery records in all groups were similar except, as expected, that a larger number of PE and PTD patients had smaller babies who were delivered earlier, and the PE patients had hypertension and proteinuria. The SEC analysis detected the presence of PP13 in the cargo of the PEVs and on their surface, in addition to the known soluble fraction. The median soluble PP13 was not significantly different across the PE, PTD, and term delivery control groups. However, after depleting the PEV of their proteome, the total PP13 (soluble and PEV-associated) was augmented in the cases of preterm PE, reaching 2153 pg/mL [IQR 1866-2838] but not in cases of PTD reaching 1576 pg/mL [1011-2014] or term delivery groups reaching 964 pg/mL [875-1636]), p < 0.01. On the surface of the circulating PEV from PTD patients, there was a decrease in PP13. Corticosteroid treatment was accompanied by a massive depletion of PP13 from the PEV, especially in preterm PE patients. This exploratory study is, thus, the first to determine PEV-associated PP13 in maternal circulation, providing a quantitative determination of the soluble and the PEV-associated fractions, and it shows that the latter is the larger. We found an increase in the amount of PP13 carried via the PEV-associated pathway in PE and PTD patients compared to term delivery cases, which was further augmented when the patients were treated with corticosteroids, especially in preterm PE. The signal conveyed by this novel communication pathway warrants further research to investigate these two differential pathways for the liberation of PP13.
Keywords: corticosteroids; extracellular vesicles; galectin 13; placental protein 13 (PP13); preeclampsia (PE); preterm delivery (PTD); size exclusion chromatography (SEC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. No significant financial support for this work was received. There was no any source, financial or any other, that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel multiple marker microarray analyzer and methodology to predict major obstetric syndromes using surface markers of circulating extracellular vesicles from maternal plasma.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025 Jan;104(1):151-163. doi: 10.1111/aogs.15020. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025. PMID: 39607297 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced placental protein 13 (PP13) in placental derived syncytiotrophoblast extracellular vesicles in preeclampsia - A novel tool to study the impaired cargo transmission of the placenta to the maternal organs.Placenta. 2018 Jun;66:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Placenta. 2018. PMID: 29884298
-
Placental protein 13 (PP13/galectin-13) undergoes lipid raft-associated subcellular redistribution in the syncytiotrophoblast in preterm preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011 Aug;205(2):156.e1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2011.03.023. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011. PMID: 21596368 Free PMC article.
-
Placental Protein 13 (PP13) - A Placental Immunoregulatory Galectin Protecting Pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2014 Aug 20;5:348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00348. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25191322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin 13 (PP13) Facilitates Remodeling and Structural Stabilization of Maternal Vessels during Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 29;20(13):3192. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133192. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261864 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel multiple marker microarray analyzer and methodology to predict major obstetric syndromes using surface markers of circulating extracellular vesicles from maternal plasma.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025 Jan;104(1):151-163. doi: 10.1111/aogs.15020. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025. PMID: 39607297 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Profiles of Maternal Plasma Extracellular Vesicles for Prediction of Preeclampsia.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024 Oct;92(4):e13928. doi: 10.1111/aji.13928. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39347565 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-13 and Laeverin Levels Interfere with Human Fetoplacental Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 8;25(12):6347. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126347. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Than N.G., Rahman O.A., Magenheim R., Nagy B., Fule T., Hargitai B., Sammar M., Hupuczi P., Tarca A.L., Szabo G., et al. Placental protein 13 (galectin-13) has decreased placental expression but increased shedding and maternal serum concentrations in patients presenting with preterm pre-eclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Virchows Arch. 2008;453:387–400. doi: 10.1007/s00428-008-0658-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

