Effective Dipole Moment Model for Axially Symmetric C3 v Molecules: Application to the Precise Study of Absolute Line Strengths of the ν6 Fundamental of CH335Cl
- PMID: 37569499
- PMCID: PMC10418978
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512122
Effective Dipole Moment Model for Axially Symmetric C3 v Molecules: Application to the Precise Study of Absolute Line Strengths of the ν6 Fundamental of CH335Cl
Abstract
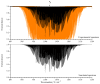
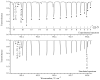
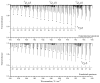
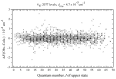
The effective dipole moment model for molecules of axial C3v symmetry is derived on the basis of the symmetry properties of a molecule which, on the one hand, is of the same order of efficiency (but much simpler and clearer in applications) as the analogous models derived on the basis of the irreducible tensorial sets theory, and, on the other hand, mathematically more correct in comparison with concepts like the Herman-Walles function used in the models. As an application of the general results obtained, we discuss high-resolution infrared spectra of CH335Cl, recorded with the Zürich prototype ZP2001 (Bruker IFS125 HR) Fourier transform infrared spectrometer at a resolution of 0.001 cm-1 and analyzed in the region of 880-1190 cm-1 (ν6 bending fundamental centered at ν0 = 1018.070790 cm-1). Absolute strengths of more than 2800 transitions (2081 lines) were obtained from the fit of their shapes both with Voigt and Hartmann-Tran profiles, and parameters of the effective dipole moment of the ν6 band were determined by the computer code SYMTOMLIST (SYMmetric TOp Molecules: LIne STrengths), created on the basis of a derived theoretical model. As the first step of the analysis of the experimental data, assignments of the recorded lines were made. A total of 5124 transitions with Jmax = 68, Kmax = 21 were assigned to the ν6 band. The weighted fit of 2077 upper energy values obtained from the experimentally recorded transitions was made with a Hamiltonian which takes into account different types of ro-vibrational effects in doubly degenerate vibrational states of the C3v-symmetric molecule. As the result, a set of 25 fitted parameters was obtained which reproduces the initial 2077 upper "experimental" ro-vibrational energy values with a root mean square deviation drms=4.7×10-5 cm-1. At the second step of the analysis, the computer code SYMTOMLIST was used for determination of the parameters of the derived effective dipole moment model. Six effective dipole moment parameters were obtained from the weighted fit procedure which reproduces absolute experimental strengths of the 2804 initial experimental transitions with a relative drms=3.4%.
Keywords: C3v-symmetry molecule; CH335Cl; absolute line positions and strengths; effective rotational and effective dipole moment operators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

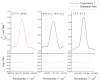
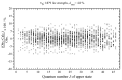
References
-
- Flaud J., Camy-Peyret C. Vibration–rotation intensities in H2O-type molecules application to the 2ν2, ν1, ν3 band of H216O. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1975;55:278–310. doi: 10.1016/0022-2852(75)90270-2. - DOI
-
- Loéte M. Devéloppement complet du moment dipolaire des molécules tétraé. Application aux bandes triplement dégénéréet a la diade ν2 et ν4. Can. J. Phys. 1983;61:1242–1259. doi: 10.1139/p83-158. - DOI
-
- Boudon V., Grigoryan T., Philipot F., Richard C., Tchana F.K., Manceron L., Rizopoulos A., Auwera J.V., Encrenaz T. Line positions and intensities for the ν3 band of 5 isotopologues of germane for planetary applications. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018;205:174–183. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2017.10.017. - DOI
-
- Tarrago J., Ulenikov O., Poussigue G. Dipole moment matrix for vibration–rotation transitions in C3v molecules. J. Phys. Paris. 1984;45:1429–1447. doi: 10.1051/jphys:019840045090142900. - DOI
-
- Saveliev V.N., Ulenikov O.N. Calculation of vibration–rotation line intensities of polyatomic molecules based on the formalism of irreducible tensorial sets. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Phys. 1987;20:67–83. doi: 10.1088/0022-3700/20/1/012. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

