Influence of a Single Deuterium Substitution for Protium on the Frequency Generation of Different-Size Bubbles in IFNA17
- PMID: 37569512
- PMCID: PMC10418495
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512137
Influence of a Single Deuterium Substitution for Protium on the Frequency Generation of Different-Size Bubbles in IFNA17
Abstract
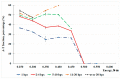
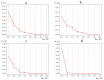
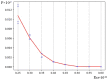
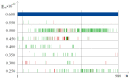
The influence of a single 2H/1H replacement on the frequency generation of different-size bubbles in the human interferon alpha-17 gene (IFNA17) under various energies was studied by a developed algorithm and mathematical modeling without simplifications or averaging. This new approach showed the efficacy of researching DNA bubbles and open states both when all hydrogen bonds in nitrogenous base pairs are protium and after an 2H-substitution. After a single deuterium substitution under specific energies, it was demonstrated that the non-coding region of IFNA17 had a more significant regulatory role in bubble generation in the whole gene than the promoter had. It was revealed that a single deuterium substitution for protium has an influence on the frequency generation of DNA bubbles, which also depends on their size and is always higher for the smaller bubbles under the largest number of the studied energies. Wherein, compared to the natural condition under the same critical value of energy, the bigger raises of the bubble frequency occurrence (maximums) were found for 11-30 base pair (bp) bubbles (higher by 319%), 2-4 bp bubbles (higher by 300%), and 31 bp and over ones (higher by 220%); whereas the most significant reductions of the indicators (minimums) were observed for 11-30 bp bubbles (lower by 43%) and bubbles size over 30 bp (lower by 82%). In this study, we also analyzed the impact of several circumstances on the AT/GC ratio in the formation of DNA bubbles, both under natural conditions and after a single hydrogen isotope exchange. Moreover, based on the obtained data, substantial positive and inverse correlations were revealed between the AT/GC ratio and some factors (energy values, size of DNA bubbles). So, this modeling and variant of the modified algorithm, adapted for researching DNA bubbles, can be useful to study the regulation of replication and transcription in the genes under different isotopic substitutions in the nucleobases.
Keywords: DNA; DNA bubbles; deuterium; dynamics of a double-stranded DNA molecule; interferon alpha-17 gene; open states; rotational movements of nitrogenous bases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Clark D.P., Pazdernik N.J., McGehee M.R. Molecular Biology. 3rd ed. Elsevier B.V.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Chapter 11—Transcription of Genes; pp. 332–361. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

