Gene-Smoking Interaction Analysis for the Identification of Novel Asthma-Associated Genetic Factors
- PMID: 37569643
- PMCID: PMC10419280
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512266
Gene-Smoking Interaction Analysis for the Identification of Novel Asthma-Associated Genetic Factors
Abstract
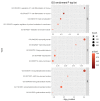
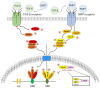
Asthma is a complex heterogeneous disease caused by gene-environment interactions. Although numerous genome-wide association studies have been conducted, these interactions have not been systemically investigated. We sought to identify genetic factors associated with the asthma phenotype in 66,857 subjects from the Health Examination Study, Cardiovascular Disease Association Study, and Korea Association Resource Study cohorts. We investigated asthma-associated gene-environment (smoking status) interactions at the level of single nucleotide polymorphisms, genes, and gene sets. We identified two potentially novel (SETDB1 and ZNF8) and five previously reported (DM4C, DOCK8, MMP20, MYL7, and ADCY9) genes associated with increased asthma risk. Numerous gene ontology processes, including regulation of T cell differentiation in the thymus (GO:0033081), were significantly enriched for asthma risk. Functional annotation analysis confirmed the causal relationship between five genes (two potentially novel and three previously reported genes) and asthma through genome-wide functional prediction scores (combined annotation-dependent depletion, deleterious annotation of genetic variants using neural networks, and RegulomeDB). Our findings elucidate the genetic architecture of asthma and improve the understanding of its biological mechanisms. However, further studies are necessary for developing preventive treatments based on environmental factors and understanding the immune system mechanisms that contribute to the etiology of asthma.
Keywords: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study; asthma; gene–environment interactions; genome-wide association study; smoking status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- GBD 2015 Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990-2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017;5:691–706. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

