Literature-Based Discovery Predicts Antihistamines Are a Promising Repurposed Adjuvant Therapy for Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37569714
- PMCID: PMC10418861
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512339
Literature-Based Discovery Predicts Antihistamines Are a Promising Repurposed Adjuvant Therapy for Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
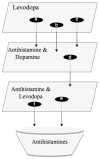
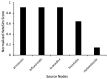
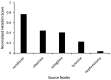
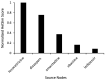
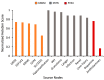
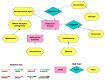
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a movement disorder caused by a dopamine deficit in the brain. Current therapies primarily focus on dopamine modulators or replacements, such as levodopa. Although dopamine replacement can help alleviate PD symptoms, therapies targeting the underlying neurodegenerative process are limited. The study objective was to use artificial intelligence to rank the most promising repurposed drug candidates for PD. Natural language processing (NLP) techniques were used to extract text relationships from 33+ million biomedical journal articles from PubMed and map relationships between genes, proteins, drugs, diseases, etc., into a knowledge graph. Cross-domain text mining, hub network analysis, and unsupervised learning rank aggregation were performed in SemNet 2.0 to predict the most relevant drug candidates to levodopa and PD using relevance-based HeteSim scores. The top predicted adjuvant PD therapies included ebastine, an antihistamine for perennial allergic rhinitis; levocetirizine, another antihistamine; vancomycin, a powerful antibiotic; captopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor; and neramexane, an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor agonist. Cross-domain text mining predicted that antihistamines exhibit the capacity to synergistically alleviate Parkinsonian symptoms when used with dopamine modulators like levodopa or levodopa-carbidopa. The relationship patterns among the identified adjuvant candidates suggest that the likely therapeutic mechanism(s) of action of antihistamines for combatting the multi-factorial PD pathology include counteracting oxidative stress, amending the balance of neurotransmitters, and decreasing the proliferation of inflammatory mediators. Finally, cross-domain text mining interestingly predicted a strong relationship between PD and liver disease.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; antihistamines; artificial intelligence; machine learning; movement disorders; repurposed drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
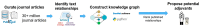
Similar articles
-
A zebrafish screen reveals Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors as neuroprotective via mitochondrial restoration in dopamine neurons.Elife. 2021 Sep 22;10:e69795. doi: 10.7554/eLife.69795. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34550070 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Effectiveness of Adjuvant Treatment With Catechol-O-Methyltransferase or Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors Compared With Dopamine Agonists Among Patients With Parkinson Disease Uncontrolled by Levodopa Therapy: The PD MED Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Neurol. 2022 Feb 1;79(2):131-140. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.4736. JAMA Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34962574 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does levodopa slow or hasten the rate of progression of Parkinson's disease?J Neurol. 2005 Oct;252 Suppl 4:IV37-IV42. doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-4008-5. J Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16222436 Review.
-
Renin-angiotensin system as a potential target for new therapeutic approaches in Parkinson's disease.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Oct;26(10):1163-1173. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1371133. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28836869 Review.
-
Behavioural and trait changes in parkinsonian patients with impulse control disorder after switching from dopamine agonist to levodopa therapy: results of REIN-PD trial.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019 Jan;90(1):30-37. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-318942. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30361296 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Cross-Domain Text Mining of Pathophysiological Processes Associated with Diabetic Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 19;25(8):4503. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084503. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674089 Free PMC article.
-
An Interpretable Machine Learning Framework for Rare Disease: A Case Study to Stratify Infection Risk in Pediatric Leukemia.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 20;13(6):1788. doi: 10.3390/jcm13061788. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38542012 Free PMC article.
-
Literature-Based Discovery to Elucidate the Biological Links between Resistant Hypertension and COVID-19.Biology (Basel). 2023 Sep 21;12(9):1269. doi: 10.3390/biology12091269. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37759668 Free PMC article.
-
Ebastine-mediated destabilization of E3 ligase MKRN1 protects against metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Jan 31;82(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05535-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39888429 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Comparative Analysis of the Overlapping Molecular Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Frontotemporal Dementia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 15;25(24):13450. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413450. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gandhi K., Saadabadi A. Levodopa (L-Dopa) StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

