Cytokine Inhibitors Upregulate Extracellular Matrix Anabolism of Human Intervertebral Discs under Alginate Beads and Alginate-Embedded Explant Cultures
- PMID: 37569715
- PMCID: PMC10418414
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512336
Cytokine Inhibitors Upregulate Extracellular Matrix Anabolism of Human Intervertebral Discs under Alginate Beads and Alginate-Embedded Explant Cultures
Abstract
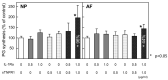
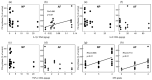
We investigated the effects of the cytokine inhibitors IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 (sTNFR1) on the extracellular matrix metabolism of human intervertebral discs (IVDs) and the roles of IL-1β and TNF in the homeostasis of IVD cells. The 1.2% alginate beads and the explants obtained from 35 human lumbar discs were treated with cytokine inhibitors. Extracellular matrix metabolism was evaluated by proteoglycan (PG) and collagen syntheses and IL-1β, TNF, and IL-6 expressions after three days of culture in the presence or absence of IL-1Ra, sTNFR1, and cycloheximide. Simultaneous treatment with IL-1Ra and sTNFR1 stimulated PG and collagen syntheses in the NP and AF cells and explants. The IL-1β concentration was significantly correlated to the relative increase in PG synthesis in AF explants after simultaneous cytokine inhibitor treatment. The relative increase in PG synthesis induced by simultaneous cytokine treatment was significantly higher in an advanced grade of MRI. Expressions of IL-1β and TNF were upregulated by each cytokine inhibitor, and simultaneous treatment suppressed IL-1β and TNF productions. In conclusion, IL-1Ra and sTNFR1 have the potential to increase PG and collagen synthesis in IVDs. IL-1β and TNF have a feedback pathway to maintain optimal expression, resulting in the control of homeostasis in IVD explants.
Keywords: autocrine; cytokine; intervertebral disc metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form were received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist delivered directly and by gene therapy inhibits matrix degradation in the intact degenerate human intervertebral disc: an in situ zymographic and gene therapy study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R83. doi: 10.1186/ar2282. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17760968 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of catabolic gene expression in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cells: implications for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R65. doi: 10.1186/ar2693. Epub 2009 May 12. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19435506 Free PMC article.
-
Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R77. doi: 10.1186/ar2275. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 17688691 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and relationship of proinflammatory chemokine RANTES/CCL5 and cytokine IL-1β in painful human intervertebral discs.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 May 15;38(11):873-80. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318285ae08. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 23660804
-
The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110660. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110660. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32853910 Review.
Cited by
-
Polysaccharide-based biomaterials for regenerative therapy in intervertebral disc degeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Dec 10;30:101395. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101395. eCollection 2025 Feb. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39759846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

