The Influence of κ-Carrageenan-R-Phycoerythrin Hydrogel on In Vitro Wound Healing and Biological Function
- PMID: 37569731
- PMCID: PMC10419105
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512358
The Influence of κ-Carrageenan-R-Phycoerythrin Hydrogel on In Vitro Wound Healing and Biological Function
Abstract
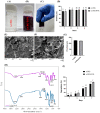
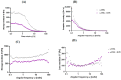
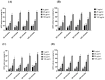
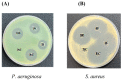
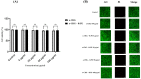
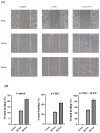
Wound healing is widely recognized as a critical issue impacting the healthcare sector in numerous countries. The application of wound dressings multiple times in such instances can result in tissue damage, thereby increasing the complexity of wound healing. With the aim of tackling this necessity, in the present study, we have formulated a hydrogel using natural polysaccharide κ-carrageenan and phycobiliprotein R-phycoerythrin from Pyropia yezoensis. The formulated hydrogel κ-Carrageenan-R-Phycoerythrin (κ-CRG-R-PE) was analyzed for its antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. The wound healing potential of the κ-CRG-R-PE was evaluated in Hs27 cells by the wound scratch assay method. The hydrogel showed dose-dependent antioxidant activity and significant antimicrobial activity at 100 μg/mL concentration. κ-CRG-R-PE hydrogels promoted more rapid and complete wound closure than κ-Carrageenan (κ-CRG) hydrogel at 24 and 48 h. κ-CRG-R-PE hydrogels also filled the wound within 48 h of incubation, indicating that they positively affect fibroblast migration and wound healing.
Keywords: R-phycoerythrin; antimicrobial activity; antioxidant activity; hydrogel; wound healing; κ-carrageenan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang C.C., Su C.H., Chen C.C. Water Absorbing and Antibacterial Properties of N-Isopropyl Acrylamide Grafted and Collagen/Chitosan Immobilized Polypropylene Nonwoven Fabric and Its Application on Wound Healing Enhancement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A. 2008;84:1006–1017. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31482. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang C.C., Su C.H., Chen J.P., Chen C.C. An Enhancement on Healing Effect of Wound Dressing: Acrylic Acid Grafted and Gamma-Polyglutamic Acid/Chitosan Immobilized Polypropylene Non-Woven. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2009;29:1715–1724. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2009.01.020. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

