Analysis of Novel Immunological Biomarkers Related to Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Severity
- PMID: 37569732
- PMCID: PMC10418816
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512351
Analysis of Novel Immunological Biomarkers Related to Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Severity
Abstract
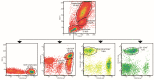
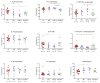
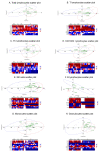
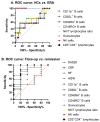
Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) are the most frequently used rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnostic markers, but they are unable to anticipate the patient's evolution or response to treatment. The aim of this study was to identify possible severity biomarkers to predict an upcoming flare-up or remission period. To address this objective, sera and anticoagulated blood samples were collected from healthy controls (HCs; n = 39) and from early RA (n = 10), flare-up (n = 5), and remission (n = 16) patients. We analyzed leukocyte phenotype markers, regulatory T cells, cell proliferation, and cytokine profiles. Flare-up patients showed increased percentages of cluster of differentiation (CD)3+CD4- lymphocytes (p < 0.01) and granulocytes (p < 0.05) but a decreased natural killer (NK)/T lymphocyte ratio (p < 0.05). Analysis of leukocyte markers by principal component analysis (PCA) and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves showed that CD45RO+ (p < 0.0001) and CD45RA+ (p < 0.0001) B lymphocyte expression can discriminate between HCs and early RA patients, while CD3+CD4- lymphocyte percentage (p < 0.0424) and CD45RA+ (p < 0.0424), CD62L+ (p < 0.0284), and CD11a+ (p < 0.0185) B lymphocyte expression can differentiate between flare-up and RA remission subjects. Thus, the combined study of these leukocyte surface markers could have potential as disease severity biomarkers for RA, whose fluctuations could be related to the development of the characteristic pro-inflammatory environment.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; NK/T lymphocyte ratio; biomarkers; central memory cells; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; disease severity; effector memory cells; leukocyte phenotype; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased effector memory CD45RA+ CD62L- CD8+ T cells and increased central memory CD45RA- CD62L+ CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(2):R91-6. doi: 10.1186/ar619. Epub 2003 Jan 6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003. PMID: 12718752 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of NK receptors CD94 and NKG2A by T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients in remission compared to active disease.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027182. Epub 2011 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22102879 Free PMC article.
-
CD45RA-Foxp3(high) activated/effector regulatory T cells in the CCR7 + CD45RA-CD27 + CD28+central memory subset are decreased in peripheral blood from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Sep 6;438(4):778-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.120. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23747721
-
Effector Functions of CD4+ T Cells at the Site of Local Autoimmune Inflammation-Lessons From Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 12;10:353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00353. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30915067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple Positivity for Anti-Citrullinated Protein Autoantibodies, Rheumatoid Factor, and Anti-Carbamylated Protein Antibodies Conferring High Specificity for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for Very Early Identification of At-Risk Individuals.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;70(11):1721-1731. doi: 10.1002/art.40562. Epub 2018 Sep 16. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29781231 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis responsive to DMARDs but with progressive bone erosion.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1254139. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1254139. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809106 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of potential biomarkers and immunoregulatory mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis based on multichip co-analysis of GEO database].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jun 20;44(6):1098-1108. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38977339 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The Differential Expressions and Associations of Intracellular and Extracellular GRP78/Bip with Disease Activity and Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;12(1):58. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12010058. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39851332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balsa A., Cabezón A., Orozco G., Cobo T., Miranda-Carus E., López-Nevot M.Á., Vicario J.L., Martín-Mola E., Martín J., Pascual-Salcedo D. Influence of HLA DRB1 alleles in the susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis and the regulation of antibodies against citrullinated proteins and rheumatoid factor. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010;12:R62. doi: 10.1186/ar2975. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huber L.C., Brock M., Hemmatazad H., Giger O.T., Moritz F., Trenkmann M., Distler J.H.W., Gay R.E., Kolling C., Moch H., et al. Histone deacetylase/acetylase activity in total synovial tissue derived from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1087–1093. doi: 10.1002/art.22512. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

