A Review on the Crosstalk between Insulin and Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling for Bone Health
- PMID: 37569816
- PMCID: PMC10419059
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512441
A Review on the Crosstalk between Insulin and Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling for Bone Health
Abstract
A positive association between insulin resistance and osteoporosis has been widely established. However, crosstalk between the signalling molecules in insulin and Wingless (Wnt)/beta-(β-)catenin transduction cascades orchestrating bone homeostasis remains not well understood. The current review aims to collate the existing evidence, reporting (a) the expression of insulin signalling molecules involved in bone-related disorders and (b) the expression of Wnt/β-catenin signalling molecules involved in governing insulin homeostasis. The downstream effector molecule, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3β), has been identified to be a point of convergence linking the two signal transduction networks. This review highlights that GSK3β may be a drug target in the development of novel anabolic agents and the potential use of GSK3β inhibitors to treat bone-related disorders.
Keywords: GSK3β; bone loss; glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; type 1 diabetes mellitus; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
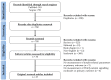
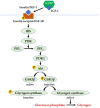
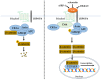
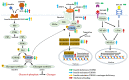
References
-
- Campillo-Sánchez F., Usategui-Martín R., Ruiz-de Temiño Á., Gil J., Ruiz-Mambrilla M., Fernández-Gómez J.M., Dueñas-Laita A., Pérez-Castrillón J.L. Relationship between Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), Trabecular Bone Score (TBS), and Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (3D-DXA) in Non-Diabetic Postmenopausal Women. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:1732. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061732. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

