Innovative Approaches for Food: Using Natural Phenolic-Rich Extracts to Produce Value-Added Fresh Pasta
- PMID: 37569826
- PMCID: PMC10419937
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512451
Innovative Approaches for Food: Using Natural Phenolic-Rich Extracts to Produce Value-Added Fresh Pasta
Abstract
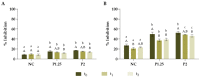
Cereal-based products, which are rich in carbohydrates, are widely consumed worldwide; however, this type of food lacks other nutrients. Phenolic compounds from natural sources, such as Moringa oleifera, can be incorporated into these products to increase their nutritional and biological value. In this study, a phenolic-rich extract was obtained from M. oleifera leaf powder using a Soxhlet extractor. The extract obtained presented a total phenolic content of 79.0 mg of gallic acid equivalents/g and the ABTS and DPPH assays showed that the extract can act as an anti-oxidant agent, with IC50 values of 205.2 mg/L and 636.0 mg/L, respectively. Afterwards, fresh pasta was produced and the extract was incorporated into the pasta to improve its biological properties and extend its shelf-life. The results demonstrated that the addition of M. oleifera to the fresh pasta increased its anti-oxidant capacity and did not interfere with the cooking properties of the product. Moreover, the fortified pasta presented an increased shelf-life, since the extract conferred protection against microbial contamination for longer periods of time. Therefore, these findings showed that the incorporation of phenolic-rich extracts from natural sources (such as M. oleifera) is a feasible sustainable biotechnological approach to produce value-added cereal-based products.
Keywords: antioxidants; bioactive compounds; cereal-based products; food fortification; fresh pasta; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- McSweeney P.L.H., Day L. Reference Module in Food Science. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016. Food Products and Ingredients. - DOI
-
- Bianchi F., Tolve R., Rainero G., Bordiga M., Brennan C.S., Simonato B. Technological, nutritional and sensory properties of pasta fortified with agro-industrial by-products: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021;56:4356–4366. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15168. - DOI
-
- Shahidi F. Functional Foods: Their Role in Health Promotion and Disease Prevention. J. Food Sci. 2004;69:R146–R149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb10727.x. - DOI
-
- Dahiya D., Terpou A., Dasenaki M., Nigam P.S. Current status and future prospects of bioactive molecules delivered through sustainable encapsulation techniques for food fortification. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023;1:500–510. doi: 10.1039/D3FB00015J. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

