TET Family Members Are Integral to Porcine Oocyte Maturation and Parthenogenetic Pre-Implantation Embryogenesis
- PMID: 37569830
- PMCID: PMC10419807
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512455
TET Family Members Are Integral to Porcine Oocyte Maturation and Parthenogenetic Pre-Implantation Embryogenesis
Abstract
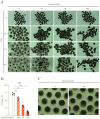
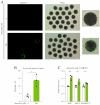
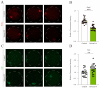
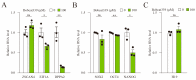
The ten-eleven translocation (TET) enzyme family, which includes TET1/2/3, participates in active DNA demethylation in the eukaryotic genome; moreover, TET1/2/3 are functionally redundant in mice embryos. However, the combined effect of TET1/2/3 triple-gene knockdown or knockout on the porcine oocytes or embryos is still unclear. In this study, using Bobcat339, a specific small-molecule inhibitor of the TET family, we explored the effects of TET enzymes on oocyte maturation and early embryogenesis in pigs. Our results revealed that Bobcat339 treatment blocked porcine oocyte maturation and triggered early apoptosis. Furthermore, in the Bobcat339-treated oocytes, spindle architecture and chromosome alignment were disrupted, probably due to the huge loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC)and concurrent increase in 5-methylcytosine (5mC). After Bobcat339 treatment, early parthenogenetic embryos exhibited abnormal 5mC and 5hmC levels, which resulted in compromised cleavage and blastocyst rate. The mRNA levels of EIF1A and DPPA2 (ZGA marker genes) were significantly decreased, which may explain why the embryos were arrested at the 4-cell stage after Bobcat339 treatment. In addition, the mRNA levels of pluripotency-related genes OCT4 and NANOG were declined after Bobcat339 treatment. RNA sequencing analysis revealed differentially expressed genes in Bobcat339-treated embryos at the 4-cell stage, which were significantly enriched in cell proliferation, cell component related to mitochondrion, and cell adhesion molecule binding. Our results indicated that TET proteins are essential for porcine oocyte maturation and early embryogenesis, and they act by mediating 5mC/5hmC levels and gene transcription.
Keywords: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine; 5-methylcytosine; Bobcat339; TET proteins; embryo; oocyte; pig.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

