IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-New Insight into Immunohepatotoxicity of Different Chronic Liver Diseases
- PMID: 37569857
- PMCID: PMC10419971
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512483
IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Chronic Hepatitis C and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-New Insight into Immunohepatotoxicity of Different Chronic Liver Diseases
Abstract
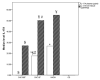
Considering the relevance of the research of pathogenesis of different liver diseases, we investigated the possible activity of the IL-23/IL-17 axis on the immunohepatotoxicity of two etiologically different chronic liver diseases. A total of 36 chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients, 16 with (CHC-SF) and 20 without significant fibrosis (CHC-NSF), 19 patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and 20 healthy controls (CG) were recruited. Anthropometric, biochemical, and immunological cytokines (IL-6, IL-10, IL-17 and IL-23) tests were performed in accordance with standard procedure. Our analysis revealed that a higher concentration of plasma IL-23 was associated with NASH (p = 0.005), and a higher concentration of plasma IL-17A but a lower concentration of plasma IL-10 was associated with CHC in comparison with CG. A lower concentration of plasma IL-10 was specific for CHC-NSF, while a higher concentration of plasma IL-17A was specific for CHC-SF in comparison with CG. CHC-NSF and CHC-SF groups were distinguished from NASH according to a lower concentration of plasma IL-17A. Liver tissue levels of IL-17A and IL-23 in CHC-NSF were significantly lower in comparison with NASH, regardless of the same stage of the liver fibrosis, whereas only IL-17A tissue levels showed a difference between the CHC-NSF and CHC-SF groups, namely, a lower concentration in CHC-NSF in comparison with CHC-SF. In CHC-SF and NASH liver tissue, IL17-A and IL-23 were significantly higher in comparison with plasma. Diagnostic accuracy analysis showed significance only in the concentration of plasma cytokines. Plasma IL-6, IL-17A and IL-23 could be possible markers that could differentiate CHC patients from controls. Plasma IL-23 could be considered a possible biomarker of CHC-NSF patients in comparison with controls, while plasma IL-6 and IL-17-A could be biomarkers of CHC-SF patients in comparison with controls. The most sophisticated difference was between the CHC-SF and CHC-NSF groups in the plasma levels of IL-10, which could make this cytokine a useful biomarker of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: IL-23/IL-17 axis; chronic hepatitis C; immunohepatotoxicity; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- CDC National Vital Statistics Reports. [(accessed on 26 July 2021)];2021 July; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/leading-causes-of-death.htm.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

